Hana - Parallel Query
Thread pools Configuration
Two thread pools control the parallelism of statement execution.
- SQLExecutors: Front End SQL receiver, execute OLTP query, delegate OLAP query to Job executor
- and JobExecutors: Execute parallel, complex OLAP query
SQLExecutor:
- Handle incoming request
- Execute Simple Statement (OLTP)
- Delegate Complex Query to the JobExecutor pool
JobExecutor:
- Execute Complex Statement as parallelized job
- Assign Jobs to available thread
Parameters
SQL Executor: indexserver.ini.
- sql_executors - min target number of threads that can be busy(default # of available thread)
- max_sql_executors - max number of threads that can be busy. Not set by default so that new threads are created to handle incoming requests.
Parameters for JobExecutor
JobExecutor: global.ini or indexserver.ini.
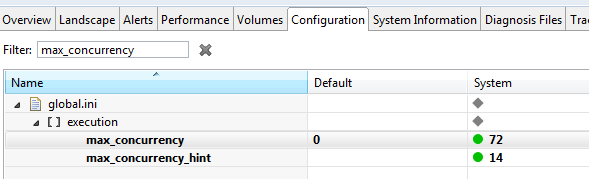
- max_concurrency - max target number of threads that can be busy. Note that from SPS12, this parameter should only need to be modified for multitenant database container installations.
- max_concurrency_hint - Limit concurrency hint even if more active job workers would be available.
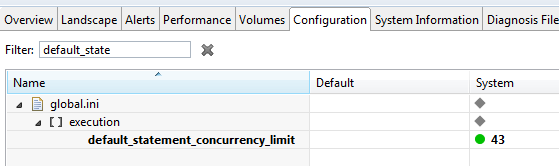
- default_statement_concurrency_limit - Used to restrict the actual degree of parallel execution per connection within a statement.
Hint
Parallelism Stopen HINT Details - MAX_CONCURRENCY Controls concurrency. This setting only accepts the value 1 (single thread plan execution) and the Join Engine determines suitable parallelism by default.
Examples:
SELECT * FROM T1 WITH HINT( MAX_CONCURRENCY(1) );
DOP
SPS11.
SAP auto-determines degree of parallelism statement execution with max parallelization.
Degree of Parallelism:
- default: best effort: unlimited use of threads for parallel statement execution
- can be controlled by statement thread limit per statement in workload classes.
- default_statement_concurrency_limit (global.ini)
8 means max 8 threads can be engaged at any one time for any one statement.
Execution Priority
Job Executor parameter that set the execution priority for a connection (ie for a statement)
alter user SYSTEM set parameter PRIORITY = '9';
select priority from m_connections where connection_id = CURRENT_CONNECTION;
Workload Class
workload class permits to limit also the parallelism.