Java - Access Modifier (private, public, …)
About
What is the visibility of language elements (ie Private vs Public)? in Java.
Access level modifiers determine whether other classes can use a particular field or invoke a particular method.
There are two levels of access control:
- At the top level: public, or package-private (no explicit modifier).
- At the member level: public, private, protected, or package-private (no explicit modifier).
Articles Related
Level
Top
A class may be declared with the modifier public, in which case that class is visible to all classes everywhere. If a class has no modifier (the default, also known as package-private), it is visible only within its own package.
Member
At the member level, you can also use the public modifier or no modifier (package-private) just as with top-level classes, and with the same meaning.
For members, there are two additional access modifiers: private and protected. The private modifier specifies that the member can only be accessed in its own class. The protected modifier specifies that the member can only be accessed within its own package (as with package-private) and, in addition, by a subclass of its class in another package.
Access to members permitted by each modifier for different group of class
| Modifier / Type of class | The Class itself | A class of the same Package | A Subclass outside of the package | World All others classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| public | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| protected | Y | Y | Y | N |
| no modifier | Y | Y | N | N |
| private | Y | N | N | N |
where:
- the Class column is the class itself
- the Package column are classes in the same package as the class (regardless of their parentage)
- the Subclass column is subclasses of the class declared outside its package
- the World column are all classes
Access levels affect you in two ways:
- when you use classes that come from another source, such as the classes in the Java platform, access levels determine which members of those classes your own classes can use.
- when you write a class, you need to decide what access level every member variable and every method in your class should have.
Example
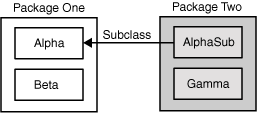
The following figure shows the four classes in this example and how they are related.
The following table shows where the members of the Alpha class are visible for each of the access modifiers that can be applied to them.
| Modifier / Classes | Alpha | Beta | Alphasub | Gamma |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| public | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| protected | Y | Y | Y | N |
| no modifier | Y | Y | N | N |
| private | Y | N | N | N |
Tips on Choosing an Access Level
If other programmers use your class, you want to ensure that errors from misuse cannot happen. Access levels can help you do this.
- Use the most restrictive access level that makes sense for a particular member. Use private unless you have a good reason not to.
- Avoid public fields except for constants. (Many of the examples in the tutorial use public fields. This may help to illustrate some points concisely, but is not recommended for production code.) Public fields tend to link you to a particular implementation and limit your flexibility in changing your code.