About
A class provides the blueprint for objects; you create an object from a class. All classes are derived from the Object class.
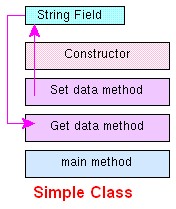
A class declaration names the class and encloses the class body between braces. The class name can be preceded by modifiers. The class body contains:
- and constructors
for the class.
In the Java programming language, every application start in a class with the help of the main method.
A class uses:
- fields to contain state information
- and uses methods to implement behaviour.
Constructors that initialize a new instance of a class use the name of the class and look like methods without a return type.
Every application begins with a class definition (the main class) with a main method.
A class is a blueprint or prototype from which objects are created.
Within an instance method or a constructor, “this” is a reference to the current object.
You control access to classes and members in the same way: by using an access modifier such as public in their declaration.
Articles Related
Special Type Class
Name
A class name must be a binary name as defined by The Java™ Language Specification.
Examples of valid class names include:
- “java.lang.String”
- “javax.swing.JSpinnerDefaultEditor”
- “java.security.KeyStoreBuilderFileBuilder1”
- “java.net.URLClassLoader31”
With the name following the Pascal Casing. (ie wiki/CamelCase which always begins with a capital letter)
Literal
Below string class is a class literal.
Class<String> c = String.class;
A class literal can be passed among methods to communicate both:
- compile-time
- and runtime type information (Used intensively with reflection)
In this case, it is called a type token
See also: Design Pattern - Typesafe heterogeneous container (Java)
Declaration
Minimal
The most basic form of a class definition is:
class MyClass {
//field, constructor, and method declarations
}
The keyword class begins the class definition for a class named MyClass and the class body (the area between the braces) contains all the code that provides for the life cycle of the objects created from the class:
- constructors for initializing new objects,
- declarations for the fields that provide the state of the class and its objects,
- and methods to implement the behaviour of the class and its objects.
You can add at the very beginning modifiers like:
- public (other classes can access MyClass)
- or private
Extend
class MyClass extends MySuperClass implements YourInterface {
//field, constructor, and method declarations
}
means that MyClass is a subclass of MySuperClass and that it implements the YourInterface interface.
Implement
Modifier
Load
Main
A start or main class is the first entry point of a whole application. She must have a main method in order to start the application. She is defined in the manifest file.
version
For the java version that have compiled the class, see Java - Compile (class file)
Type
Enclosing
An enclosing class is a static inner class
Instantiation
For every type of object, the Java virtual machine instantiates an immutable instance of java.lang.Class which:
- provides the ability to create new classes and objects.
- is the entry point for all of the Reflection APIs.
Management
Dependency
a class when an instance of an object is available
The simplest way is to invoke Object.getClass().
the class
String
For instance, this statement will returns the Class for String in the Class nicoStringClass .
Class nicoStringClass = "nico".getClass();
Console
Class c = System.console().getClass();
There is a unique console associated with the virtual machine which is returned by the static method System.console(). The value returned by getClass() is the Class corresponding to java.io.Console.
Enumeration
enum E { A, B }
Class c = A.getClass();
A is is an instance of the enum E; thus getClass() returns the Class corresponding to the enumeration type E.
Array
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
Class c = bytes.getClass();
Since arrays are Objects, it is also possible to invoke getClass() on an instance of an array. The returned Class corresponds to an array with component type byte.
Support
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError:
HelloWorldApp.java.
Check your classpath. Your class cannot be found.
Unsupported major.minor version
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: myClass: Unsupported major.minor version 51.0
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass1(Native Method)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClassCond(ClassLoader.java:631)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.defineClass(ClassLoader.java:615)
at java.security.SecureClassLoader.defineClass(SecureClassLoader.java:141)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.defineClass(URLClassLoader.java:283)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.access$000(URLClassLoader.java:58)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:197)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:190)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:306)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:301)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:247)
Could not find the main class: myClass. Program will exit.
be sure to use the good JRE Version.