Java - (Collection|container) Framework (Types)
About
A collection (known also as a container) is an object that groups multiple objects (elements) into a single unit.
Collections are used to store, retrieve, manipulate, and communicate aggregate data.
A collections framework is a unified architecture for representing and manipulating collections.
In Java, a collection implements the iterable interface.
Example
- a poker hand (a collection of cards),
- a mail folder (a collection of letters),
- a telephone directory (a mapping of names to phone numbers).
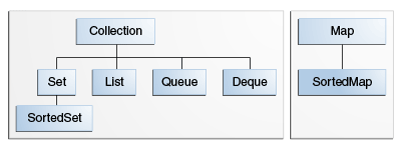
Interface Hierarchy
The core collection interfaces form a hierarchy. A Set is a special kind of Collection, A SortedSet is a special kind of Set.
The collection interfaces are divided into two groups:
- The javase/9/docs/api/java.util.Collection.html interface (The most basic one),
- The javase/9/docs/api/java.util.Map.html interface. A Map is not a true Collection. These interfaces contain collection-view operations.
Mappings are not collections and collections are not mappings (Elements of a map elements are well known “Key-value pairs”)
We have then two tree.
All the core collection interfaces are generic.
Collection
The root of the collection hierarchy. A collection represents a group of objects known as its elements. The Collection interface is the least common denominator that all collections implement and is used to pass collections around and to manipulate them when maximum generality is desired.
Some types of collections:
- allow duplicate elements, and others do not.
- are ordered and others are unordered.
The Java platform doesn't provide any direct implementations of the Collection interface but provides implementations for the following sub-interfaces:
| Data Type | Allow Duplicate | Ordered |
|---|---|---|
| java.util.List | Yes | Yes |
| java.util.Set | No | No |
| java.util.SortedSet | No | Yes (Ascending) |
| java.util.Map | No | No |
| java.util.SortedMap | No | Yes (Ascending) |
Set
Set is a collection that cannot contain duplicate elements.
List
An ordered collection (sometimes called a sequence). Lists can contain duplicate elements. The user of a List generally has precise control over where in the list each element is inserted and can access elements by their integer index (position). If you've used Vector, you're familiar with the general flavor of List.
See List
Queue
A collection used to hold multiple elements prior to processing. Besides basic Collection operations, a Queue provides additional insertion, extraction, and inspection operations.
Queues typically, but do not necessarily, order elements in a FIFO (first-in, first-out) manner. Among the exceptions are priority queues, which order elements according to a supplied comparator or the elements' natural ordering.
Whatever the ordering used, the head of the queue is the element that would be removed by a call to remove or poll. In a FIFO queue, all new elements are inserted at the tail of the queue. Other kinds of queues may use different placement rules. Every Queue implementation must specify its ordering properties.
Deque
Queue - deque (Double Ended Queue)
See also the Deque Interface section.
Map
An object that maps keys to values. A Map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. If you've used Hashtable, you're already familiar with the basics of Map.
SortedMap — a Map that maintains its mappings in ascending key order. This is the Map analog of SortedSet. Sorted maps are used for naturally ordered collections of key/value pairs, such as dictionaries and telephone directories.
Variant
To keep the number of core collection interfaces manageable, the Java platform doesn't provide separate interfaces for each variant of each collection type. Instead, the modification methods in each interface are designated optional. If an unsupported operation is invoked, a collection throws an UnsupportedOperationException.
Variant List:
- (Unmodifiable|Modifiable). Unmodifiable Collections do not support modification operations (such as add, remove and clear) Collections that are not unmodifiable are modifiable.
- Append-only. An implementation that doesn't support the remove operations. Logs (such as error logs, audit logs and journals for recoverable data objects) are natural append-only sequences.
- (Immutable|Mutable). Immutable Collections guarantee that no change in the Collection object will be visible. Collections that are not immutable are mutable. Collections that cannot be changed by the client AND will never change for any other reason. It allows multiple threads to access a collection concurrently without the need for synchronization.
- (Fixed-sized|variable-size) Lists guarantee that their size remains constant even though the elements can change. Lists that are not fixed-size are referred to as variable-size.
- (Random|sequential) access lists. Lists that support fast (generally constant time) indexed element access are known as random access lists. Lists that do not support fast indexed element access are known as sequential access lists. The RandomAccess marker interface enables lists to advertise the fact that they support random access. This enables generic algorithms to change their behaviour to provide good performance when applied to either random or sequential access lists.
Implementation
The preferred style is to choose an implementation (interface) when a Collection is created and to immediately assign the new collection to a variable of the corresponding interface type (or to pass the collection to a method expecting an argument of the interface type). In this way, the program does not become dependent on any added methods in a given implementation, leaving the programmer free to change implementations anytime that it is warranted by performance concerns or behavioral details.
Most commonly used implementation:
| Interface | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Set | HashSet |
| List | ArrayList |
| Map | HashMap |
| Queue | LinkedList |
| Deque | ArrayDeque |
How to
test the Collection Type of an object
if (myObject instanceof Collection<?>){
}
Query engine
With index and all: https://github.com/npgall/cqengine
Big Data Implementation
Ie: collections over primitive types
The Trove maps/sets use open addressing instead of the chaining approach taken by the JDK hashtables.