Linear Algebra - Scalar (Multiplication|Product) - Scaling
About
Scalar Multiplication (Scaling) is the multiplication of a vector (for instance <math>v_a</math> ) by a scalar (real number) (for instance <math>\alpha</math> ) to produce another vector (for instance <math>v_b</math> )
<math>f (v_a) = \alpha.v_a = v_b</math>
Multiplying a vector v by a scalar <math>\alpha</math> is defined as multiplying each entry of v by <math>\alpha</math> :
<math>\alpha.v = \alpha[v_{[1]},v_{[2]},\dots,v_{[n]}] = [\alpha.v_{[1]},\alpha.v_{[2]}, \dots ,\alpha.v_{[n]}]</math>
<math>v. \alpha</math> is not legal whereas <math>\alpha . v</math> is.
Scalar Multiplication is used to define a line
Articles Related
Property
Scalar multiplication is:
- Associative: <math>\alpha(\beta.v) = (\alpha.\beta)v</math>
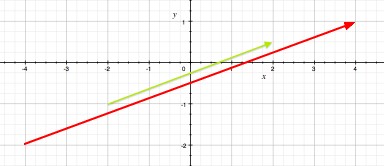
Geometric Representation
The green arrow represents the vector [4, 1.5] and the red arrow represents two times this vector.
- Scalars bigger than 1 give rise to somewhat larger copies of the original vector
- Scalars smaller than 1 give rise to somewhat smaller copies of the original vector
- Negative scalars give rise to vectors pointing in the opposite direction
Computation
2 [5, 4, 10] = [2 x 5, 2 x 4, 2 x 10] = [10, 8, 20]
Python:
def scalarVectorMult(alpha, v): return [alpha*x for x in v]