Docker - docker-machine
About
Docker machine is deprecated for swarm and the command are now merged into the docker command under the swarm command
# before
docker-machine init
# after
docker swarm init
See docker/machine
Docker Machine is a command line client that lets you
- manage your Docker host (virtual host or machine, daemon)
- and install Docker Engine on them.
You can use Machine to create Docker hosts:
- on your local Mac or Windows box,
- on your company network, in your data center,
- or on cloud providers like AWS or Digital Ocean.
You can use Docker Machine to:
- Install and run Docker on Mac or Windows
- Provision and manage multiple remote Docker hosts
- Provision Swarm clusters
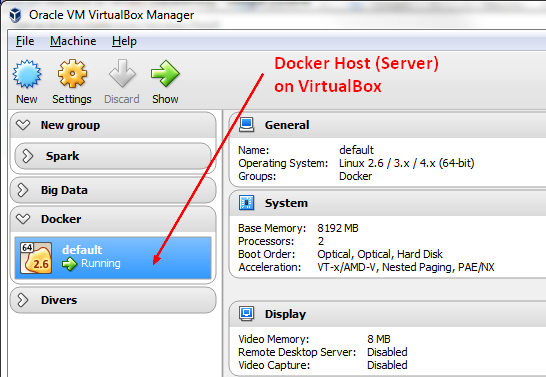
Docker Machine uses Boot2Docker to initialise, start, stop and delete the VirtualBox's VM right from the command line.
The host operating system is boot2docker.
Management
List your machines.
$ docker-machine ls
- On my machine
NAME ACTIVE DRIVER STATE URL SWARM DOCKER ERRORS
default virtualbox Timeout
- From the doc:
NAME ACTIVE DRIVER STATE URL SWARM
dev * virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.100:2376
my-docker-machine virtualbox Stopped
default virtualbox Stopped
Important: If you are using Docker for Mac or Docker for Windows, you can skip this step.
Create your machine
If you are using Docker for Mac or Docker for Windows, you can skip this step.
Example:
docker-machine create \
--driver virtualbox \
--virtualbox-memory 8192 \
--virtualbox-disk-size "40960" \
default
Modify the configuration
docker-machine stop
VBoxManage modifyvm default --cpus 2
VBoxManage modifyvm default --memory 8192
docker-machine start
Ssh
docker-machine ssh
## .
## ## ## ==
## ## ## ## ## ===
/"""""""""""""""""\___/ ===
~~~ {~~ ~~~~ ~~~ ~~~~ ~~~ ~ / ===- ~~~
\______ o __/
\ \ __/
\____\_______/
_ _ ____ _ _
| |__ ___ ___ | |_|___ \ __| | ___ ___| | _____ _ __
| '_ \ / _ \ / _ \| __| __) / _` |/ _ \ / __| |/ / _ \ '__|
| |_) | (_) | (_) | |_ / __/ (_| | (_) | (__| < __/ |
|_.__/ \___/ \___/ \__|_____\__,_|\___/ \___|_|\_\___|_|
Boot2Docker version 1.12.3, build HEAD : 7fc7575 - Thu Oct 27 17:23:17 UTC 2016
Docker version 1.12.3, build 6b644ec
docker@default:~$ exit
Remove machine
$ docker-machine rm my-docker-machine
Successfully removed my-docker-machine
IP
docker-machine ip
192.168.99.100
Three ways to find the IP dependent of your configuration
Name
On windows, you can use the name host.docker.internal to reach the host.
Nat
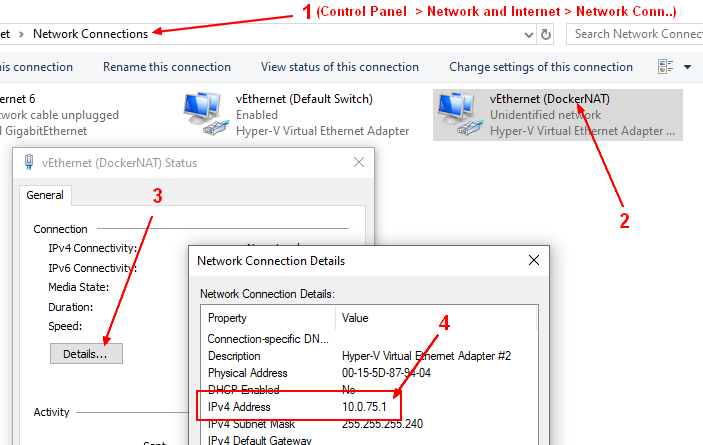
If you are using a NAT, to determine the Docker Windows host IP interface (By default, this is the interface named vEthernet (DockerNAT) on the IP 10.0.75.1)
- at the command line with netsh
netsh interface ip show addresses
# and to filter for one interface
netsh interface ip show addresses "vEthernet (DockerNAT)"
Configuration for interface "vEthernet (DockerNAT)"
DHCP enabled: No
IP Address: 10.0.75.1
Subnet Prefix: 10.0.75.0/24 (mask 255.255.255.0)
InterfaceMetric: 15
- Windows graphically
Docker Machine
docker-machine ip default
192.168.99.100
The DOCKER_HOST environment variable contains also the IP adress of the host
This IP is assigned by the docker-machine create subcommand.
Metadata Location
On Windows, all the metadata (disk, config) are stored at:
C:\Users\user\.docker\machine\machines\machineName
# Example
C:\Users\gerard\.docker\machine\machines\default