Computer Clock - Clock Tick (Clock Cycle)
About
CPU's are marching forward at some frequency, and the period of this frequency is called a Clock Tick or Clock Cycle
A 100Mhz processor will receive 100,000,000 clock ticks every second.
Articles Related
Management
Creation
The tick is managed/created by the clock generator
Stop
Processor clocks may stop ticking under circumstances like the following:
- The processor is halted when there is nothing for the CPU to do. For example, the processor may halt to save power while the computer is servicing an I/O request. When Intel Hyper-Threading Technology is enabled, both logical processors must be halted for performance-monitoring counters to be powered down.
- The processor is asleep as a result of being halted or because of a power-management scheme. There are different levels of sleep. In the some deep sleep levels, the time-stamp counter stops counting.
Count
The count of cycles, also known as clockticks, forms the basis for measuring how long a program takes to execute. See CPU - (CPU|Processor) Time Counter
Clockticks are also used as part of efficiency ratios like cycles per instruction (CPI).
Each core on a modern CPU has a TSC (Timestamp counter) that counts the number of ticks that have transpired.
Example: 2,59 times per nanosecond.
Property: Invariant: guarantee that the frequency will not change.
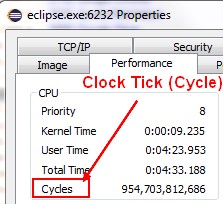
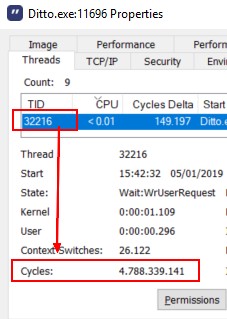
Process Explorer
Clock Tick in process explorer:
- for a process
Assembly
You can read the TSC (Timestamp counter) with the rdtsc assembly instruction.
Documentation / Reference
- Vol3 18.7 - Counting clocks https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/intel-sdm