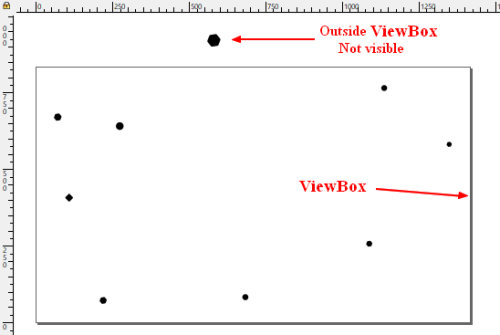
SVG - View Box
About
The Viewbox attribute specifies:
- a boundary box in which only the inside elements are visible.
- and how to resize / fit its content when the viewport is changing.
In conjunction with the preserveaspectratio attribute, it provides the capability to stretch an SVG viewport to fit a particular container element.
Syntax
The viewBox specify a rectangle in user space which should be mapped to the bounds of the viewport established by the given element
The value of the ‘viewBox’ attribute is a list of four numbers separated by whitespace and/or a comma
min-x min-y width height
where:
| Name | Domain (in abstract user units) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| <min-x> | positive/negative number | x coordinate of the left top corner of the view box |
| <min-y> | positive/negative number | y coordinate of the left top corner of the view box |
| <width> | > 0 - number | width of the viewport rectangle |
| <height> | >0 - number | height of the viewport rectangle |
A number 1) is defined as being an integer or a decimal
Default
Without viewbox, the default viewbox value is browser dependent and is generally:
0 0 300 150
Demo:
- A circle of 50 rayon located at (60,60)
<svg style="border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
- We calculate the SVG width and height dimension to show the view box
let svg = document.getElementsByTagName("svg")[0].getBoundingClientRect();
console.log("The default viewbox of the SVG (minus 2 times a border of 1) for this browser is "+(svg.width-2*1)+" x "+(svg.height-2*1));
- Output where you can see the default view box and its calculation
Standalone: Setting the height or width
Without the viewbox
If you set the width or the height, you will expand or cut the viewport depending on the value of the default viewbox
Example:
- with a 50px width, the circle didn't feet in the view port 0 0 50 100 and is cut
<svg width="50px" style="border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
- with a 150px width, the circle feet in the view port 0 0 150 100 and is not cut
<svg width="150px" style="border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
With the viewbox
With the viewbox, the circle stretches and fits into the given height
<svg height="50px" viewBox="0 0 150 150" style="border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
In a container: preserveAspectRatio
In a container, the preserveAspectRatio attribute control how the svg will fit in it.
none without width and height
With preserveAspectRatio value of none without any CSS definition, the SVG will starts from the container width, conserve its shape and then overflow the container on the y axis.
<div style="width:300px;height:100px">
<svg viewBox="0 0 150 150" preserveAspectRatio="none" style="border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
</div>
none with CSS width and height
To constraint the shape to stay in its container, you need to tell CSS that the value of width and hieght should be calculate from the container. below we have added the width:100%;height:100% CSS properties on the SVG.
With a preserveAspectRatio value of none, the shape will fit but without preserving the ratio between the width and height.
<div style="width:300px;height:100px">
<svg viewBox="0 0 150 150" preserveAspectRatio="none" style="width:100%;height:100%;border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
</div>
xMidYMid meet
With a preserveAspectRatio value of xMidYMid meet (the default, therefore not specified), the shape will fit and the the ratio will be preserved between the width and height, preserving the shape of the geometry.
<div style="width:300px;height:100px">
<svg width="400px" viewBox="0 0 150 150" style="width:100%;height:100%;max-width:200px;border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
</div>
Note that setting:
- the width on the svg has no impact at all
- the max-width permits to constraint the width (same for max-height)
More preserveAspectRatio
Below is a simple illustration on the effect of preserveAspectRatio based on the possible values from the specification
Example with the value xMinYmin meet
<div style="width:400px;height:100px">
<svg preserveAspectRatio="xMinYMin meet" viewBox="0 0 150 150" style="width:100%;height:100%;border: 1px solid #D5D8CB;">
<circle cx="60" cy="60" r="50" fill="#D5D8CB" stroke="#ECDCC6" stroke-width="5"/>
</svg>
</div>
Transformation
Unlike the transform, the automatic transformation that is created due to a ‘viewBox’ does not affect the following attributes on the element with the ‘viewBox’ attribute.
- the coordinates ‘x’, ‘y’,
- the dimension ‘width’ and ‘height’
On the other hand, like the transform attribute, it does establish a new coordinate system for all other attributes and for descendant elements.
minx and miny
On an outermost svg element, a translate transformation will be needed if the ‘viewBox’ attributes specifies values other than zero for <min-x> or <min-y>.