About
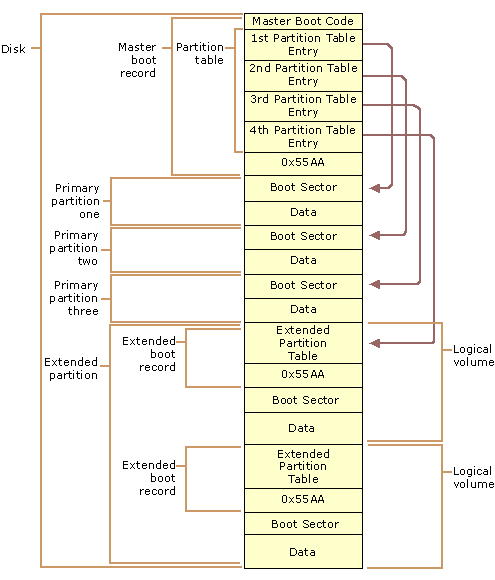
Hard disks can be divided into one or more logical disks called partition. This division is described in the partition table found in sector 0 of the disk.
Articles Related
Syntax
Name
The partition is the last part of the disk name.
For example, /dev/sda1 is the first partition on the first hard disk in the system.
See also:
- Linux kernel documentation (the Documentation/devices.txt file).
Table
The partition data are saved in a partition table found in sector 0 of the disk.
Usage
Linux needs at least one partition, namely for its root file system. It can use swap files and/or swap partitions, but the latter are more efficient. So, usually one will want a second Linux partition dedicated as swap partition.
On Intel compatible hardware, the BIOS that boots the system can often only access the first 1024 cylinders of the disk.
For this reason people with large disks often create a third partition, just a few MB large, typically mounted on /boot, to store the kernel image and a few auxiliary files needed at boot time, so as to make sure that this stuff is accessible to the BIOS. There may be reasons of security, ease of administration and backup, or testing, to use more than the minimum number of partitions.
Type
partition type can be one of:
- “primary”,
- or “extended”.
Most partitions are primary partitions. If you have more than one partition, the first usable partition (one that can hold data) is almost always a primary.
Management
Partition utility that modify the partition table
- fdisk (The fdisk or sfdisk command will not list any partition size larger than 2TB.)
Create
If you want to create, remove, or resize a partition, the device can not be in use (partitions can not be mounted, and swap space can not be enabled). The easiest way to achieve this it to boot your system in rescue mode.
with parted
(parted) mkpart
Partition type? primary/extended? primary
File system type? [ext2]?
Start? 34.4GB
End? 68.7GB
where:
- part-type is one of: primary, extended, logical. Extended and logical are only used for msdos and mips disk labels.
- fs-type can be one of “btrfs”, “ext2”, “ext3”, “ext4”, “fat16”, “fat32”, “hfs”, “hfs+”, “linux-swap”, “ntfs”, “reiserfs”, or “xfs”.
Parted doesn't create a filesystem. The filesystem type is only used to determine the partition type.
Once a partition has been created, you create a file system on it. See Linux - File System
Remove
If you want to create, remove, or resize a partition, the device can not be in use (partitions can not be mounted, and swap space can not be enabled). The easiest way to achieve this it to boot your system in rescue mode.
Resize
If you want to create, remove, or resize a partition, the device can not be in use (partitions can not be mounted, and swap space can not be enabled). The easiest way to achieve this it to boot your system in rescue mode.
With:
The only way to change a partition size using fdisk is by deleting and recreating it. How to Resize a Partition using fdisk
List
See File System - Partition table (Sector 0)
Example:
- with parted. The below will list all partition on all disk
parted -l
- with lsblk
sudo lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
fd0 2:0 1 4K 0 disk
sda 8:0 0 128G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 500M 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 127.5G 0 part /
sdb 8:16 0 128G 0 disk
├─sdb1 8:17 0 128G 0 part /mnt/resource
└─sdb2 8:18 0 512B 0 part
sdc 8:32 0 128G 0 disk
└─sdc1 8:33 0 128G 0 part /opt/infa
Know the different partition type
Command (m for help): l
0 Empty 1e Hidden W95 FAT1 80 Old Minix bf Solaris
1 FAT12 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 39 Plan 9 82 Linux swap / So c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 3c PartitionMagic 83 Linux c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
4 FAT16 <32M 40 Venix 80286 84 OS/2 hidden C: c7 Syrinx
5 Extended 41 PPC PReP Boot 85 Linux extended da Non-FS data
6 FAT16 42 SFS 86 NTFS volume set db CP/M / CTOS / .
7 HPFS/NTFS 4d QNX4.x 87 NTFS volume set de Dell Utility
8 AIX 4e QNX4.x 2nd part 88 Linux plaintext df BootIt
9 AIX bootable 4f QNX4.x 3rd part 8e Linux LVM e1 DOS access
a OS/2 Boot Manag 50 OnTrack DM 93 Amoeba e3 DOS R/O
b W95 FAT32 51 OnTrack DM6 Aux 94 Amoeba BBT e4 SpeedStor
c W95 FAT32 (LBA) 52 CP/M 9f BSD/OS eb BeOS fs
e W95 FAT16 (LBA) 53 OnTrack DM6 Aux a0 IBM Thinkpad hi ee EFI GPT
f W95 Ext'd (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a5 FreeBSD ef EFI (FAT-12/16/
10 OPUS 55 EZ-Drive a6 OpenBSD f0 Linux/PA-RISC b
11 Hidden FAT12 56 Golden Bow a7 NeXTSTEP f1 SpeedStor
12 Compaq diagnost 5c Priam Edisk a8 Darwin UFS f4 SpeedStor
14 Hidden FAT16 <3 61 SpeedStor a9 NetBSD f2 DOS secondary
16 Hidden FAT16 63 GNU HURD or Sys ab Darwin boot fb VMware VMFS
17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 64 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
18 AST SmartSleep 65 Novell Netware b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid auto
1b Hidden W95 FAT3 70 DiskSecure Mult bb Boot Wizard hid fe LANstep
1c Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX be Solaris boot ff BBT
Mount
A partition is not mounted. A file system is. See File System mount