About
du is a disk usage tool that estimates file space usage by subfolder.
It exists also as Technet edition
- Windows: cleanmgr.exe Free also the %temp% directory.
See also Linux - disk free command (df)
Syntax
du [OPTION]... [FILE]...
du [OPTION]... --files0-from=F
Options
Data Filtering
- -a, –all: get info for all files, not just directories
- --max-depth=N: print the total for a directory (or file, with --all) only if it is N or fewer levels below the command line argument; --max-depth=0 is the same as --summarize
- -X FILE, --exclude-from=FILE: Exclude files that match any pattern in FILE.
- --exclude=PATTERN Exclude files that match PATTERN.
Summarize
- -s, --summarize display only a total for each argument
- -c, --total: produce a grand total
Calculation
- -S, --separate-dirs do not include size of subdirectories
- --apparent-size: print apparent sizes, rather than disk usage; although the apparent size is usually smaller, it may be larger due to holes in (“sparse”) files, internal fragmentation, indirect blocks, and the like
Symlink
- -l, --count-links: show sizes many times if hard linked
- -L, --dereference: dereference all symbolic links
- -P, --no-dereference: don’t follow any symbolic links (this is the default)
Formatting
Time
- --time show time of the last modification of any file in the directory, or any of its subdirectories
- --time=WORD show time as WORD instead of modification time: atime, access, use, ctime or status
- --time-style=STYLE show times using style STYLE:
- full-iso,
- long-iso,
- iso,
- +FORMAT FORMAT is interpreted like ‘date’
Newline
- -0, --null: end each output line with 0 byte rather than newline
Size
- -h, --human-readable: print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G)
- --si like -h, but use powers of 1000 not 1024
- --block-size=SIZE: display the size as a multiple of SIZE. Shortcut
- -b: bit --block-size=SIZE
- -k: --block-size=1k
- -m: --block-size=1M
Difference between du and df
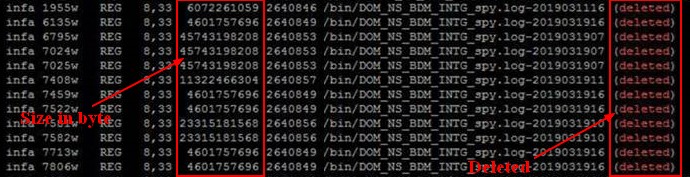
du shows the space by file whereas df shows the space by block of file.
If there is a big difference in their output, try to see if some deleted file are not held by a process as open.
Example with linux and lsof
lsof /device | grep -i deleted
If this is the case, you need to restart the process to reclaim this buffers.
Snippet
Top space
To find the top space users in a directory
du -k | sort -n
Show larger than specified size
- larger than 100MB
du -h -t 100M -a
get sizes of each file
du -a tmp
4 tmp/testFile.txt
8 tmp
get total size of a folder
- with –max-depth=0
du --max-depth=0 ~
6167480 /home/oracle
- with the s option
du -s ~
6167480 /home/oracle
get size of each sub folder
- with –max-depth=1
du -h --max-depth=1
get sub-folder total size of containing files only (without sub-folder size)
$ du -Sc --max-depth=1 ~
8 /home/oracle/jos
20 /home/oracle/.ssh
20 /home/oracle/index_advisor
4 /home/oracle/.mozilla
345688 /home/oracle/112272_diag
36276 /home/oracle/.dropbox-dist
4 /home/oracle/.gconf
4 /home/oracle/.gnome
4 /home/oracle/.dbus
20 /home/oracle/.dropbox
4 /home/oracle/.gnome2
4 /home/oracle/.gnome2_private
4 /home/oracle/.java
20 /home/oracle/.vnc
400 /home/oracle/linux8664
8 /home/oracle/bea
8 /home/oracle/.gconfd
12 /home/oracle/oraInventory
173020 /home/oracle/crash
16 /home/oracle/.dropbox-master
256 /home/oracle/Dropbox
4 /home/oracle/.config
4 /home/oracle/oradiag_oracle
4842736 /home/oracle
6167480 total