About
A memory/storage hierarchy in computer storage distinguishes each level in the hierarchy by:
- and generally by the distance between the storage device and the CPU.
The transfer of memory from primary storage to secondary storage is done through virtual memory.
Storage levels
There are three major storage levels
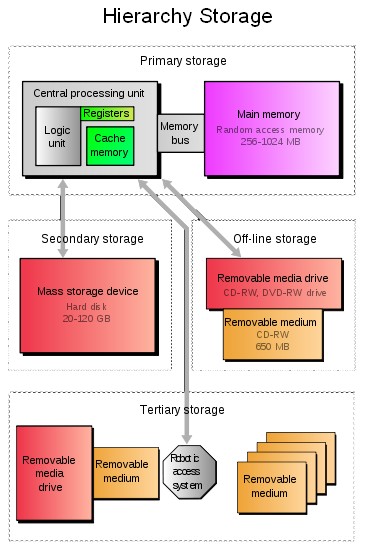
Primary
-
- Processor registers – fastest possible access (usually 1 CPU cycle), only hundreds of bytes in size
- Level 1 (L1) cache – often accessed in just a few cycles, usually tens of kilobytes
- Level 2 (L2) cache – higher latency than L1 by 2× to 10×, often 512 KiB or more
- Level 3 (L3) cache – higher latency than L2, often 2048 KiB or more
- the main memory system RAM and controller cards – may take hundreds of cycles, but can be multiple gigabytes. Access times may not be uniform, in the case of a NUMA machine.
Secondary
Secondary storage and On-line mass storage principally Disk storage – millions of cycles latency if not cached, but very large
Tertiary
Tertiary and Off-line bulk storage - several seconds latency, can be huge because it happens via a network connection.
Name
Internal / External
The internal or external type of memory is a grouping by location of the memory.
When the memory is internal, it's on the motherboard, otherwise, it's external.
There is only one internal memory and it's the primary (main/internal).
| Level | Type |
|---|---|
| Primary | Internal |
| Secondary | External |
| Tertiary | External |
Main / Auxiliary
Historically, memory and storage were respectively called main memory and auxiliary storage.
Auxiliary storage (or auxiliary memory units) is used to represent memory which are not directly accessible by the CPU (ie secondary or tertiary storage).
Volatile / Non-volatile
Memory can also be categorized by their volatility.