About
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a language for representing information about resources.
RDF is based on the idea of identifying things using Web identifiers (called Uniform Resource Identifiers, or URIs), and describing resources in terms of simple properties and property values.
This enables RDF to represent simple statements about resources as a graph of nodes and arcs representing the resources, and their properties and values.
The semantic graphs Model complex real-world relationships beyond Boolean in the data as a graph. They are then used in social networks and social interactions by linking disparate data sets.
As the notion of row does not exist for RDF data (the relationship applies for the whole data set (table), new data relationships can be added without restructuring the data model. The schemas can then continuously and dynamically evolve.
- Rdf : linked data
- Relational: Fact Data
Articles Related
Resources
Web metadata
- the title, author, and modification date of a Web page,
- copyright and licensing information about a Web document,
- or the availability schedule for some shared resource.
Non Web
- information about items available from on-line shopping facilities (e.g., information about specifications, prices, and availability)
- the description of a Web user's preferences for information delivery.
Syntax and representation
The RDF terms for the various parts of this statement
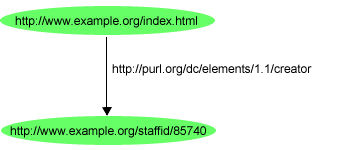
http://www.example.org/index.html has a creator whose value is John Smith
are:
- the subject is the URL http://www.example.org/index.html
- the predicate is the word “creator”
- the object is the phrase “John Smith”
that could be represented by an RDF statement with their respective URI having:
- a subject http://www.example.org/index.html
- a predicate http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/creator
- and an object http://www.example.org/staffid/85740
Graph
that could be represented within the RDF's graph model (See concept guide) by:
- a node for the subject
- a node for the object
- an arc for the predicate, directed from the subject node to the object node.
Xml
<rdf:RDF>
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://../Marcus">
<rdf:type rdf:resource="http://../Person"/>
<p:hasName ..="">Marcus</c:name>
<p:hasAge ..="">38</c:age>
<p:hasGender ..="">Male</c:gender>
</rdf:Description>
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://../FloridaSwamp">
<rdf:type rdf:resource="http://../NaturalFeature"/>
<c:hasLocation>Florida</c:location> ...
</rdf:Description>
...
</rdf:RDF>
Table
| Subject | Property | Object |
|---|---|---|
| p:Marcus | rdf:type | rc:Person |
| p:Marcus | pred:hasName | Marcus |
| p:Marcus | pred:hasAge | 38 |
| c:AcmeCorp | rdf:type | rc:Organization |
| .. | .. | .. |
Getting Started
This Primer is designed to provide the reader with the basic knowledge required to effectively use RDF.
Concept
- Linked Data - Connect Distributed Data across the Web. Linked Data is about using the Web to connect related data that wasn't previously linked.
- Semantic Web The Semantic Web is about two things. It is about common formats for integration and combination of data drawn from diverse sources, where on the original Web mainly concentrated on the interchange of documents. It is also about language for recording how the data relates to real world objects. That allows a person, or a machine, to start off in one database, and then move through an unending set of databases which are connected not by wires but by being about the same thing.
- RDF introduces an enterprise metadata framework. The metadata graph associates underlying data, process and domain models based on their semantics. Linking of resources (via metadata registries) enables interoperability between apps that exchange data.
Open Source Tools
- Jena: Java API Library,
- Cytoscape. Network Data Integration, Analysis, and Visualization in a Box.
- Fuseki (Previously Joseki). Fuseki is a SPARQL server. It provides REST-style SPARQL HTTP Update, SPARQL Query, and SPARQL Update using the SPARQL protocol over HTTP.
- Sesame is an extensible Java framework for storing, querying and inferencing for RDF. It can be deployed as a web server or used as a Java library. Features include several query languages (SeRQL and SPARQL),
- ARQ,
- TDB,
- SDB,
- Pellet,
- D2RQ,
- Jetty,
- GATE,
- Protégé…
Reference / Documentation
Home Page:
Documentation / Specification: