Android - Content Provider
About
A content provider is a facade between the data store (Xml, Database) and the applications.
Articles Related
Benefits
- Change the underlying data source without changing the application code
- Leverage standard android library. SyncAdapters, Loaders and CursorsAdapters use ContentProvider. SimpleCursorAdapter
- Allow others apps to access your data source securely (because of the content provider).
Steps
- get Permission to use the Content Provider
- Access and perform sime data operation (query, insert, update, delete)
- Display a feedback (Information ,…)
Built-In Content Provider
- Calendar Provider Guide Calendar API URI: CalendarContract;Calendars.CONTENT_URI
- internal audio store: MediaStore.Audio.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI
- …
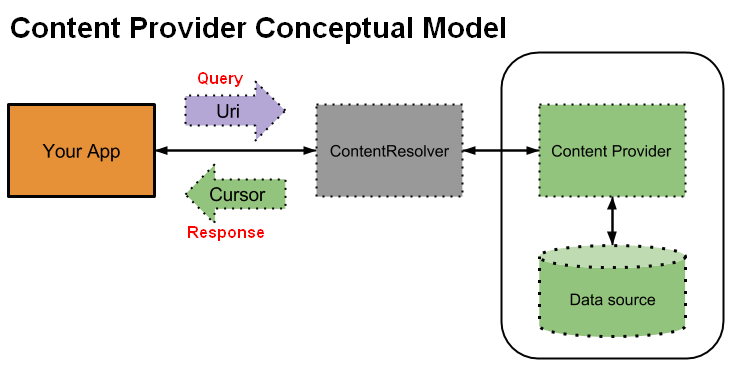
Model
Content URI
The content URI, see:
content://com.example.packageName:Location:Query
where:
- Scheme: content. It refers to a content provider
- Authority: A unique string use to locate the content provider (generally the package name of the application)
- Location: Which generally points to a database table
- Query: Optional. Ex: 1234?date=201260807
Manipulation example:
// The authority
public static final String CONTENT_AUTHORITY = "com.example.packageName";
// The location
public static final String PATH_LOCATION = "location";
// The content base URI
public static final Uri BASE_CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse("content://" + CONTENT_AUTHORITY);
// The URI content with location
public static final Uri CONTENT_URI = BASE_CONTENT_URI.buildUpon().appendPath(PATH_LOCATION).build();
// Add a query path element: Use buildUpon() to obtain a builder representing an existing URI.
Uri = CONTENT_URI.buildUpon().appendPath(queryString).build();
UriMatcher
- PATH matches PATH exactly
- PATH/# matches PATH followed by a number
- PATH/* matches PATH followed by any string
- PATH/*/OTHER/# matches PATH followed by a string followed by OTHER followed by a number
reference/android/content/UriMatcher.html
Content Resolver
The content resolver locates the provider through the authority part of the content URI.
Content Resolver function mapping:
- query: Read from the data
- insert: Add to the data
- ])|update: Change preexisting data
- ])|delete: Delete from the data
Cursor
Code
In a onCreate activity function:
import android.content.ContentResolver;
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
public static final String LOG_TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Get the TextView which will be populated with the Dictionary ContentProvider data.
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView dictTextView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.dictionary_text_view);
// Get the ContentResolver which will send a message to the ContentProvider
ContentResolver resolver = getContentResolver();
// Get a Cursor containing all of the rows in the Words table
Cursor cursor = resolver.query(UserDictionary.Words.CONTENT_URI, null, null, null, null);
try {
dictTextView.append("The user dictionary contains: " + cursor.getCount() + "\n");
int idIndex = cursor.getColumnIndex(Words._ID);
int idWord = cursor.getColumnIndex(Words.WORD);
int idFrequency = cursor.getColumnIndex(Words.FREQUENCY);
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String wordRow = cursor.getString(idIndex) + " - " + cursor.getString(idWord) + " - " + cursor.getString(idFrequency) + "\n";
Log.v(LOG_TAG, wordRow);
dictTextView.append(wordRow);
}
} finally {
cursor.close();
}
}
}
Registration
Registration of the content provider with the package manager.
See The provider element in the manifest file.
<manifest >
<application>
...............
<!-- Content Authority = Normally the package of your application -->
<!-- Content Provider Class = Can be relative to the content authority package -->
<!-- android:exported="true" : the provider is shared with others application -->
<!-- android:permission. When exported="true" a license permission can be given -->
<provider
android:authorities="CONTENT AUTHORITY"
android:name="CONTENT PROVIDER CLASS"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="com.myapp.license"
/>
</application>
<!-- android:permission. When exported="true" a license permission can be given -->
<permission
android:name="com.myapp.license"
android:protectionlevel="dangerous"
android:label="Licence description"
</permission>
</manifest>
Example:
<manifest >
<application>
...............
<provider
android:authorities="com.example.android.sunshine.app"
android:name="com.example.android.sunshine.app.data.WeatherProvider"
/>
</application>
</manifest>
Test checks to make sure that the content provider is registered correctly:
public void testProviderRegistry() {
String providerName = WeatherProvider.class.getSimpleName();
String providerClass = WeatherProvider.class.getName();
String contentAuthority = WeatherContract.CONTENT_AUTHORITY;
// Get the package manager
PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
// We define the component name based on the package name from the context and the
// WeatherProvider class.
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(mContext.getPackageName(),providerClass);
try {
// Fetch the provider info using the component name from the PackageManager
// This throws an exception if the provider isn't registered.
ProviderInfo providerInfo = pm.getProviderInfo(componentName, 0);
// Make sure that the registered authority matches the authority from the Contract.
assertEquals("Error: "+providerName+" registered with authority: " + providerInfo.authority +
" instead of authority: " + contentAuthority,
providerInfo.authority, contentAuthority);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
// I guess the provider isn't registered correctly.
assertTrue("Error: "+providerName+" not registered at " + mContext.getPackageName(),
false);
}
}