About
Latency is a performance metric also known as Response time.
Latency (Response Time) is the amount of time take a system to process a request (ie to first response) from the outside or not, remote or not,
In other words, how much time it takes between making a request and receiving the first data requested. That you can implement so: the time calculated just before sending the request to just after the first response has been received.
A request can be:
- an UI action (such as pressing a button)
- or a server API call
- …
Network Protocol analysers (such as Wireshark) measure the time when bytes are actually sent/received over the interface.
See also: Algorithm - (Performance|Running Time|Fast)
Can we answer “What was the performance?” by “It took 15 seconds. Performance’s units, “inverse seconds”, can be awkward
Articles Related
Measurement
Latency measurement is done via a timer metrics
See also: CPU - (CPU|Processor) Time Counter
Requirement
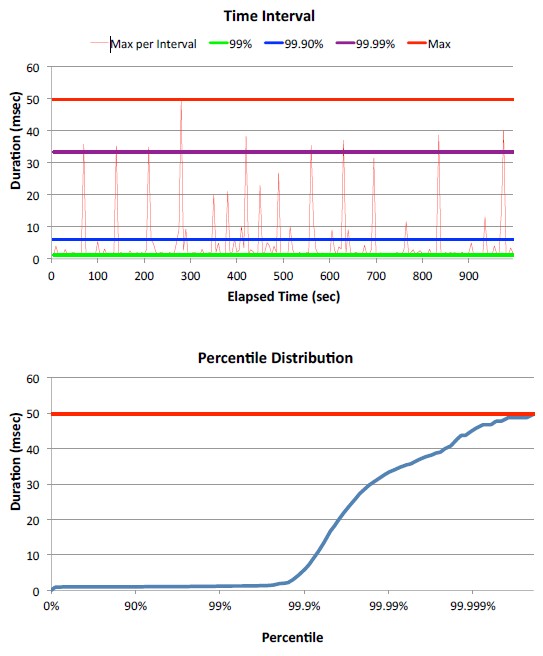
Service level expectation in percentile:
- 90% of responses should be below 0.5sec,
- 99% should be below 2 seconds,
- 99.9 should be better than 5 seconds.
- And a >10 sec. response should never happen.
If you haven’t stated percentiles and a Max, you haven’t specified your requirements
User Perception
- 100 ms: user perceives as instantaneous
- 1s: is about the upper limit of human flow of though. User loses the feeling direct feedback
- 10s: Upper limit of attention. Feedback is important and the chance of context switch is high.
Source: Response Times: The 3 Important Limits
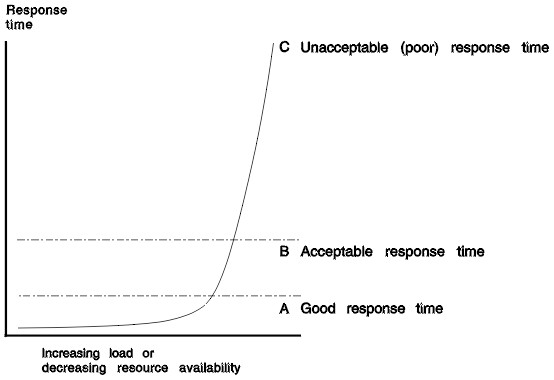
Response Time
over load
Time response over load, for a system with a uniform response time. Without a lot of variance. Ie 99.7% of the request fall in 3 standards deviations.
percentile
Storage
hdrhistogram - data structure to capture latency
See also: https://tideways.io/profiler/blog/developing-a-time-series-database-based-on-hdrhistogram
Documentation / Reference
- How NOT to Measure Latency An attempt to share wisdom…Matt Schuetze, Product Management Director, Azul Systems - Presentation on how not to measure latency, which explains why average values are better measure of latency than median values and why maximum values are very important.