About
A module is a discrete unit of functionality which you can compile, run, test and debug independently.
Modules contain everything that is required for their specific tasks:
- source code,
- build scripts,
- unit tests,
- deployment descriptors,
- and documentation.
However, modules exist and are functional only in the context of a project. Depending on the logical and functional requirements to the project, you can create:
- a single-module
- or a multi-module project.
Articles Related
Configuration
Menu Location
File > Project Structure > Module
Storage (iml file)
Configuration information for a module is stored in a .iml module file. By default, such a file is located in the module's content root folder.
Development teams, normally, share the .iml module files through version control.
The information about modules the project includes is stored in %module_name%.iml files. Module files are created for each module.
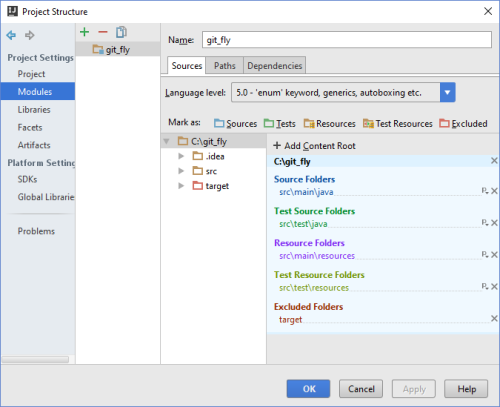
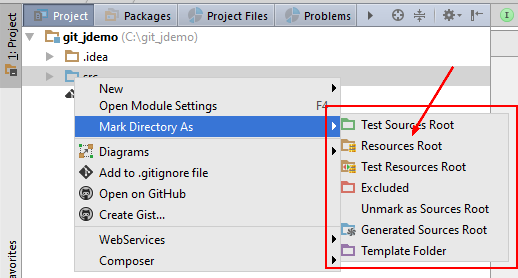
Directory Structure
Content root is a folder that contains all the files that make up your module.
Folders within a content root can be assigned to the following categories:
- Source roots (content must be compiled)
- Generated source roots (the generated source roots are not suggested as target folders on certain wizard)
- Test source roots (code intended for testing)
- Generated test source roots
- Resource roots (only in Java modules) During the build process, all the contents of the resource folders are copied to the output folder as is.
- Test resource roots
- Excluded roots (IDEA will Ignore)
Dependency
Configuration
A facet represents certain configuration, specific for a particular framework/technology, associated with a moduel. A module can have multiple facets.
List
| Module type | Description |
|---|---|
| Java Module | Encapsulates core functionality for building Java applications. The functionality of a Java module can be expanded by adding facets. |
| Web Module | Provides facilities for developing web applications using programming languages other than Java, for example, PHP, or JavaScript, or markup languages. |
| Plugin Module | Facilitates development of IntelliJ IDEA plugins. Supports IntelliJ IDEA SDK configuration and run configurations for running a dedicated IntelliJ IDEA instance for plugin debugging. |
| J2ME Module | Provides facilities for developing J2ME mobile applications, including support for various Mobile JDK and J2ME-oriented run configurations. |
| Flash Module | This module type is intended for developing Adobe Flash platform-targeted content (applications and libraries for web (Flash Player), desktop (Adobe AIR) and mobile devices (AIR mobile)). |
| Android Module | Encapsulates core functionality for developing Android applications. |
| Maven Module | Provides facilities for managing Maven projects, executing Maven goals, downloading artifacts. |
| Grails Application | Provides facilities for Grails application development. |
| Griffon Application | Provides facilities for Griffon application development. |
| The following module types are available provided that the corresponding plugins are downloaded and enabled: | |
| Ruby Module | Provides facilities for creating Ruby projects and Rails applications. |
| Python Module | Provides facilities for Python, Django and Google App Engine development. |