About
With a stratify function, you can turn a series of CSV record in a JSON tree object.
Since v4
Articles Related
Steps
Creating the stratify operator
In the stratify object definition, you may change the following properties:
- the parentId function must return the parent of the node. For the root node, the parent id should be undefined. (Null and the empty string are equivalent to undefined.)
- the id, the id of the node. For leaf nodes, the id may be undefined; otherwise, the id must be unique.
var stratify = d3.stratify()
.parentId(function (d) {
return d.path.substring(0, d.path.lastIndexOf("\\"));
})
.id(function (d) {
return d.path;
});
Getting the data as CSV
A template string containing the CSV data is passed to the d3.csvParse function. See D3 - DSV
var data = d3.csvParse(`path,size
root,0
root\\child1,10
root\\child2,20
`);
console.log("Data:")
console.log(data)
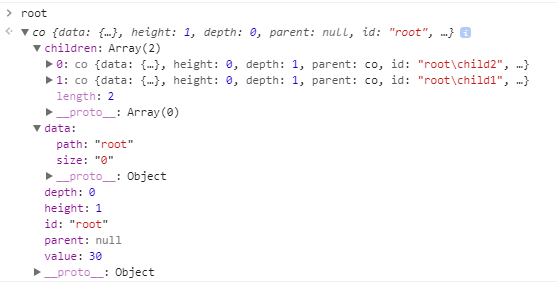
Creating the tree (By calling the stratify operator)
In this step, you call the stratify operator with the d3 CSV in-memory data representation as parameter to create a tree that will have:
- a children property. An array of nodes
- a depth property (0 for the root to N for the leaves)
- a height property which is the inverse of the depth property (N for the root to 0 for the leaves)
var stratify = d3.stratify()
.parentId(function (d) {
return d.path.substring(0, d.path.lastIndexOf("\\"));
})
.id(function (d) {
return d.path;
});
var data = d3.csvParse(`path,size
root,0
root\\child1,10
root\\child2,20
`);
var root = stratify(data);
console.log(root);
Operations on the tree
Normally, you go further and you call two tree operations (See D3 - Hierarchy):
- sum that will add for each node the value property
- sort that will sort the children
var stratify = d3.stratify()
.parentId(function (d) {
return d.path.substring(0, d.path.lastIndexOf("\\"));
})
.id(function (d) {
return d.path;
});
var data = d3.csvParse(`path,size
root,0
root\\child1,10
root\\child2,20
`);
var root = stratify(data);
root.sum(function (d) {
return +d.size;
})
.sort(function (a, b) {
return b.height - a.height || b.value - a.value;
});
console.log(root);