D3 - Csv Function (CSV from an URL)
About
This section talks about the function d3.csv that parse a CSV file. To parse a CSV string, see D3 - DSV.
Reference: Csv
Articles Related
Prerequisites
- The csv file or string must be rfc 4180 compliant
Properties
- The mime type of the request is “text/csv”.
- The request is processed asynchronously, such that the method returns immediately after opening the request.
A common mistake is to include references to the external data outside of the callback function. This may cause problem because the function is asynchronous. To prevent problems, make sure to reference your data only from within the callback function (or from within other functions that you call within the callback function).
- D3 employed the first row of the CSV for property names, and subsequent rows for values.
Syntax
Csv
d3.csv(url[[, accessor], callback])
where:
- URL: Default to relative.
- An optional accessor function may be specified, which is then passed to d3.csv.parse
- callback is a function invoked with as the argument the parsed rows or null if an error occurs.
var dataset; //Global var
d3.csv(url, function(error, data) {
// If error is not null, something went wrong.
if (error) {
console.log(error); //Log the error.
} else {
console.log(data); //Log the data.
dataset = data; // Give the data a global scope
//Call some other functions that generate the visualization
}
});
Text
Csv is an alias to the text function.
d3.text(url, 'text/csv', function(rawData) {
// Remove comment rows with regex (Starting with the # characters)
rawData = rawData.replace( /^[#][^\r\n]+[\r\n]+/mg , '');
// Parse the text as csv
csvData = d3.csv.parse(rawData);
// Continue
}
);
with How to use Regular expression (Regexp) in Javascript?
Example
Name,Age
Nicolas,42
Rixt,39
Madelief,10
Melissa,6
- Script
d3.csv("https://gerardnico.com/datafile/basic_d3.csv", function(data) {
// Process the data, for instance
for (var i=0;i<data.length;i++) {
console.log(data[i].Name+" is "+data[i].Age+" years.");
}
});
- Output:
Debugging
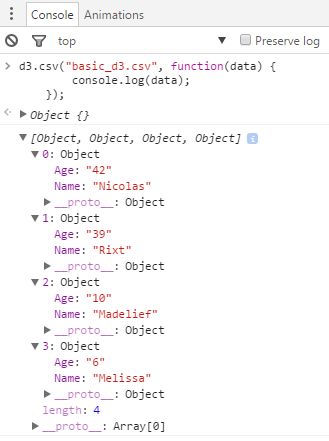
You can see the data array by sending it to the console log
d3.csv("basic_d3.csv", function(data) {
console.log(data);
});
Example from the devtools of chrome: