About
Time series functions in OBIEE.
The implementation of the time serie function is based on the time dimension. ( See set up time dimensions)
At query time, the Oracle BI Server then generates SQL that pushes the time offset processing down to the database whenever possible.
Before using these functions on a particular dimension, you have to set up the time dimension
Articles Related
Implementation
- First, set up time dimensions based on the period table in your data warehouse.
- Then, you can define measures with the time serie function:
- AGO,
- TODATE,
- and PERIODROLLING from 11g
.
Use and grain
Limitation, use :
- You may only enter AGO and TODATE functions in the Expression Builder in the Administration Tool.
- You cannot use them in coded SQL.
- Functions are for relational data sources only
The Ago and ToDate functions allow you use Expression Builder to call a logical function to perform time series calculations instead of aliasing physical tables and modeling logically.
The time series functions calculate Period Ago and Period to Date functions based on user supplied calendar tables, not on standard SQL date manipulation functions.
The following list describes the important grains in navigating a time query, using the following query example:
Select quarter, YearAgoSales
- Query grain. The grain of the request. In the query example, the query grain is Quarter.
The grain of a cube in the business model is the combination of the most detailed levels it supports (for instance Day x Product x Office x Sales Rep x Customer. At query time, measures can always be aggregated to higher levels, such as Year x Brand x Company, which is referred to as the “query grain.”
- Time Series grain. The grain at which the aggregation is requested. In the query example, the Time Series grain is Year. Note that the PERIODROLLING function does not have a time series grain; instead, you specify a start and end period in the function.
Time series query is valid only if the time series grain is at the query grain or higher
- Storage grain. The query in the example can be computed from daily sales or from monthly sales, or from quarterly sales. The grain of the aggregate source is called aggregation grain.
The chronological key has to be defined at this level
Functions
Ago
OBIEE 10G/11G - Period to period comparison with the AGO Function
PERIODROLLING
The PERIODROLLING function does not have a time series grain; instead, you specify a start and end period in the function.
The PERIODROLLING function lets you perform an aggregation across a specified set of query grain periods, rather than within a fixed time series grain. The most common use is to create rolling averages.
Note that because this function has no time series grain, the length of the rolling sequence is determined by the query grain. For example, “Dollars 3-Period Rolling Average” averages:
- the last 3 months if the query grain is Month,
- the last 3 years if the query grain is Year.
In Expression Builder, the PERIODROLLING function has the following template:
PeriodRolling(<<Measure>>, <<Starting Period Offset>>, <<Ending Period Offset>>)
Using this function template, you can create the following expression for the measure:
PeriodRolling("Sales"."Base Measures"."Dollars" , -2, 0)
The expression for the 3-month rolling average is:
PeriodRolling("Sales"."Base Measures"."Dollars" , -2, 0) /3
It is usually a mistake to use the AVG function to create a rolling average. AVG computes the average of the database rows accessed at the storage grain, but you need an average where the denominator is the number of rolling periods at the query grain.
Note that the PERIODROLLING function includes a fourth optional hierarchy argument that lets you specify the name of a hierarchy in a time dimension, such as yr, mon, day, that you want to use to compute the time window. This option is useful when there are multiple hierarchies in a time dimension, or when you want to distinguish between multiple time dimensions.
ToDate
The TODATE function accumulates the measure from the beginning of the time series grain period to the current displayed query grain period.
TODATE aggregates a measure attribute from the beginning of a specified time period to the currently displayed time.
If unsupported metrics are requested, NULL values will be returned and a warning entry will be written to the NQQuery.log file when the logging level equals three or above.
A TODATE function may not be nested within another TODATE function.
You can nest exactly one TODATE and multiple Ago functions if they each have the same level argument.
Syntax:
TODATE(<measure_expression>, <level>)
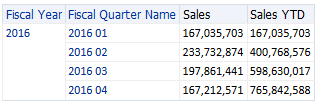
For example, this function can calculate Year to Date sales. A sort of rolling total sum into the level (Year, Quarter, Month) by time column.
Implementation:
To calculate the TODATE measure, it seems that OBIEE basically performs the following steps:
- create an additional query on the TODATE measure with the grain of the report and the grain of the TODATE function.
- get the data and sums the measure up in a rolling fashion for the grain level of the TODATE function
- perform a internal join on the baseline column
Example of SQL:
SELECT
SUM( C_SALES.SALES ) AS c1
, D_TIME.FISCAL_QUARTER_NAME AS c2
, D_TIME.FISCAL_YEAR_NAME AS c3
FROM
D_TIME
, C_SALES
WHERE
(
D_TIME.FISCAL_YEAR_NAME = '2016'
AND D_TIME.TIME_DIMENSION_KEY = C_SALES.D_TIME
)
GROUP BY
D_TIME.FISCAL_YEAR_NAME
, D_TIME.FISCAL_QUARTER_NAME;