About
The login level is a parameter which control the number of information that you will retrieve in the log file from nothing (level 0 - no_log_found) to a lot of information (level 5).
You can enable logging level for individual users, you cannot configure a logging level for a group.
In normal operations :
- users have a logging level set to 0
- administrator have a logging level set to 2
Articles Related
Description of logging levels
| Logging Levels | Logging Level Information That Is Logged |
|---|---|
| Level 0 | No logging |
| Level 1 | Logs the SQL statement issued from the client application Logs elapsed times for query compilation, query execution, query cache processing, and back-end database processing Logs the query status (success, failure, termination, or timeout). Logs the user ID, session ID, and request ID for each query |
| Level 2 | Logs everything logged in Level 1 Additionally, for each query, logs the repository name, business model name, presentation catalog (called Subject Area in Answers) name, SQL for the queries issued against physical databases, queries issued against the cache, number of rows returned from each query against a physical database and from queries issued against the cache, and the number of rows returned to the client application |
| Level 3 | Logs everything logged in Level 2 Additionally, adds a log entry for the logical query plan, when a query that was supposed to seed the cache was not inserted into the cache, when existing cache entries are purged to make room for the current query, and when the attempt to update the exact match hit detector fails |
| Level 4 | Logs everything logged in Level 3 Additionally, logs the query execution plan. |
| Level 5 | Logs everything logged in Level 4 Additionally, logs intermediate row counts at various points in the execution plan. |
How to set a logging level ?
For one request (Temporary log level)
You might want to diagnose performance or data issues by setting a temporary log level for a query. You can enable query logging for a specific query by preceding your Select statement with the following:
Set Variable LOGLEVEL=n;
This instruction sets the loglevel system session variable only for this SQL.
See the following example:
Set Variable LOGLEVEL=5; select year, product, sum(revenue) from time, products, facts
For this query, the logging level of five is used regardless of the value of the underlying LOGLEVEL variable.
See this article to see how to do : OBIEE - How and where can I set a Request variable (SET VARIABLE) ?
System
Available in 11G
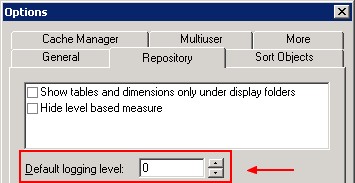
You can find a default logging level in the option of the repository:
This option determines the default query logging level for the internal BISystem user.
A query logging level of 0 (the default) means no logging. Set this logging level to 2 to enable query logging for internal system processes like event polling and initialization blocks.
For one user
loglevel session variable
By setting the loglevel system session variable via an initialization block, you can control the loglevel of each user.
The loglevel must be an integer datatype
user dialog
The session variable LOGLEVEL overrides a user's logging level. For example, if the Oracle BI Administrator has a logging level defined as 4 and LOGLEVEL is defined as default 0 (zero) in the repository, the Oracle BI Administrator's logging level will be 0.
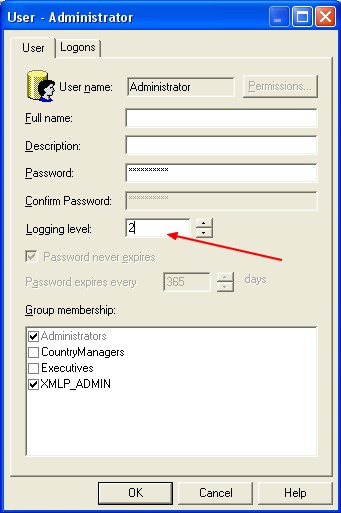
- In the Administration Tool, select Manage > Security (10g) or Identity (11g). The Security Manager dialog box appears.
- Double-click the user's user ID. The User dialog box appears.
- Set the logging level by clicking the Up or Down arrows next to the Logging Level field.
odbc functions
Through the call of ODBC functions, you can see and set session variables included LOGLEVEL.
Example on how to:
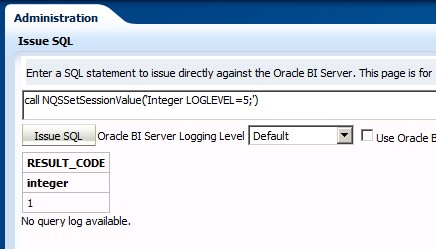
- set the log level to 5 with the issue SQL facility
call NQSSetSessionValue('Integer LOGLEVEL=5;')
- get its value:
call NQSGetSessionValues('NQ_SESSION.LOGLEVEL')
For a group
You cannot configure a logging level for a group.