About
The Bi Server interface functions permit:
- to get data dictionary information.
- to manage the query cache
- to set a repository session variable
You can call them :
- through a client that provides OBIEE.
- through a Java or ODBC code.
Articles Related
Bi Server Data dictionnary Functions
NQSGetLevelDrillability
NQSGetLevelDrillability returns context-specific drill-down information.
{call NQSGetLevelDrillability('SELECT "Sales Facts"."Amount Sold" saw_0, Channels."Channel Desc" saw_1,
Promotions."Promo Category" saw_2 FROM SH ORDER BY saw_1, saw_2')}
NQSGenerateDrillDownQuery
NQSGenerateDrillDownQuery return context-specific drill-down information.
{call NQSGenerateDrillDownQuery('SELECT "Sales Facts"."Amount Sold" saw_0, Channels."Channel Desc" saw_1,
Promotions."Promo Category" saw_2 FROM SH ORDER BY saw_1, saw_2')}
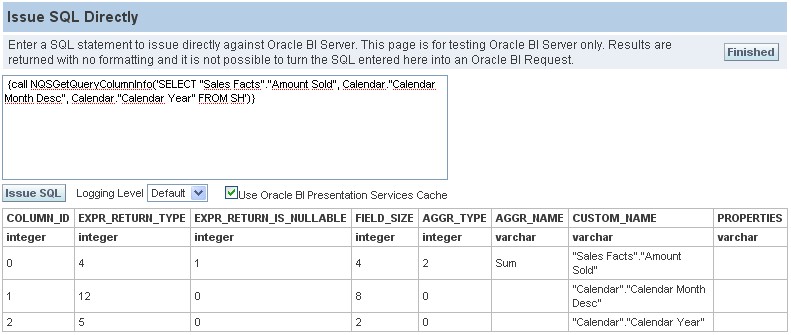
NQSGetQueryColumnInfo
{call NQSGetQueryColumnInfo('SELECT "Sales Facts"."Amount Sold", Calendar."Calendar Month Desc",
Calendar."Calendar Year" FROM SH')}
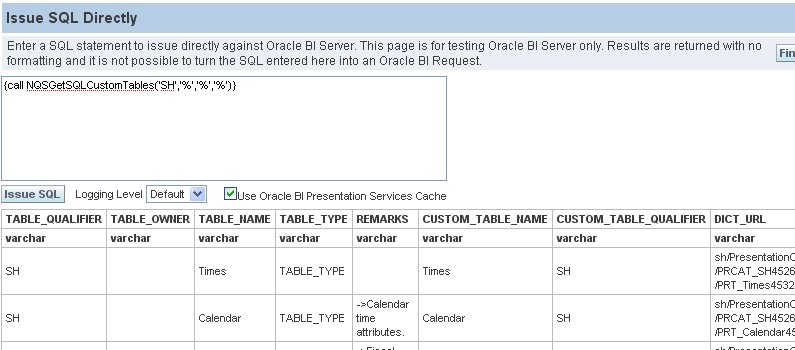
NQSGetSQLCustomTables
{call NQSGetSQLCustomTables('SH','%','%','%')}
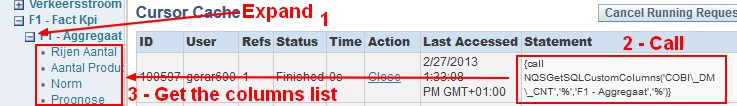
NQSGetSQLCustomColumns
{call NQSGetSQLCustomColumns('SH','%','Table','%')}
BI Server cache
Only administrators have the right to purge cache. Therefore, scripts that call these ODBC-extension functions must run under credentials with administrator privileges.
If there is a single quote within the string argument of a procedure, then you must use another single quote to escape it.
A result code is returned after you issue a purge cache command.
| Result Code | Result Message |
|---|---|
| 1 | SAPurgeCacheByDatabase returns successfully |
| 59115 | Operation not performed because caching is not enabled. |
| 59116 | The database specified does not exist |
| 59117 | The table specified does not exist |
| 85025 | The physical cube specified does not exist |
The following ODBC functions affect BI Server cache entries associated with the repository specified by the ODBC connection:
SAPurgeCacheByQuery
Purges a cache entry that exactly matches a specified query. For example, using the following query, you would have a query cache entry that retrieves the names of all employees earning more than 100,000:
select lastname, firstname from employee where salary > 100000;
The following call programmatically purges the cache entry associated with this query:
Call SAPurgeCacheByQuery('select lastname, firstname from employee where salary > 100000' );
SAPurgeCacheByTable
Purges all cache entries associated with a specified physical table name (fully qualified) for the repository to which the client has connected.
This function takes up to four parameters representing the four components (database, catalog, schema and table name proper) of a fully qualified physical table name. For example, you might have a table with the fully qualified name of DBName.CatName.SchName.TabName. To purge the cache entries associated with this table in the physical layer of the analytics repository, execute the following call in a script:
Call SAPurgeCacheByTable( 'DBName', 'CatName', 'SchName', 'TabName' );
Wild cards are not supported by the Analytics Server for this function. Additionally, DBName and TabName cannot be null. If either one is null, you will receive an error message.
SAPurgeAllCache
Purges all cache entries. The following is an example of this call:
Call SAPurgeAllCache();
SAPurgeCacheByDatabase
Purges all cache entries associated with a specific physical database name. A record is returned as a result of calling any of the ODBC procedures to purge the cache. This function takes one parameter that represents the physical database name and the parameter cannot be null. The following is an example of this call:
Call SAPurgeCacheByDatabase( 'DBName' );
SASeedQuery
Call SASeedQuery( 'select mytable.mycolumn from mySubjectArea' );
SAPurgeALLMCNCache
Purges all SAP/BW cache entries.
The following shows the syntax of this procedure:
Call SAPurgeALLIMCNCache ();
SAPurgeMCNCacheByCube
Purges all cache entries that are associated with the specified physical cube. The database name and cube name are the external names of the repository objects. The following shows the syntax of this procedure:
Call SAPurgeMCNCacheByCube( 'DBName', 'CubeName');
Presentation Services query cache
SAGetSharedRequestKey
An ODBC procedure that takes a logical SQL statement from Presentation Services and returns a request key value.
Call SAGetSharedRequestKey('sql-string-literal');
When users access Answers to run queries, Presentation Services caches the results of the queries. Presentation Services uses the request key and the logical SQL string to determine if subsequent queries can use cached results.
If the cache can be shared, then subsequent queries are not stored.
The value of the request key is affected by the following factors:
- Whether the Virtual Private Database option (VPD) has been selected in the repository physical database object
- Whether any session variables have been marked as Security Sensitive in the repository. Presentation Services takes security sensitive variable values into consideration when computing the request key for logical requests against database objects marked as Virtual Private Databases.
To manage the repository session variable
NQSSetSessionValue
Most of the case, you just need to update a session variable in the scope of a logical sql request and you can do it with a request variable
This function will modify or create a session variable with some value.
To modify a repository session variable for the entire session scope, you can fired this odbc function:
- for a number data type:
call NQSSetSessionValue('Float MyRepositoryVariable=200;')
- or for a string data type:
call NQSSetSessionValue('String MyRepositoryVariable=My Value;')
- or for a date data type:
call NQSSetSessionValue('Date Mydate=2013-04-31;')
- or for a datime data type:
call NQSSetSessionValue('Datetime MydateTime=2013-01-01 00:00:02;')
- or for an integer data type:
call NQSSetSessionValue('Integer LOGLEVEL=1;')
NQSGetSessionValues
NQSGetSessionValues returns one or more server variables.
Example:
- From a JDBC java call
Statement stmt = getConnection().prepareStatement("call NQSGetSessionValues('NQ_SESSION.USER,NQ_SESSION.GROUP')");
ResultSet s = stmt.getResultSet();
NQSessionUSer = s.getString(1);
...
The return values are truncated by the following parameter
from the section Server Section Parameters of the NQSConfig.ini:
VARIABLE_VALUE LIMIT= 10;
In this case, the name of the user can't be bigger than 10 characters.
Others
call NQSGetDirectMembers('GUID=AuthenticatedUser')
call NQSSearchIdentities('BOTH','GUID=Account Usage Role,anonymous-role,authenticated-role,BI Developer Administrator Role,BIConsumer,Contact Usage Role,Database Access Control Security,EXP Super User Role,Metadata Dictionary Role,Research Contact Usage Role,Usage Tracking Role')
Odbc driver returned an error (SQLExecDirectW).
Error Details
Error Codes: OPR4ONWY:U9IM8TAC
State: HY000. Code: 10058.
[NQODBC] [SQL_STATE: HY000]
[nQSError: 10058] A general error has occurred.
[nQSError: 43113] Message returned from OBIS.
[nQSError: 13049] User 'myUser'
with 'AtAGlance;/;oracle.bi.publisher.accessReportOutput;oracle.bi.server.manageRepositories;/;oracle.bi.scheduler.manageJobs;oracle.epm.financialreporting.editBatch;Explore;oracle.bi.publisher.administerServer;oracle.bi.publisher.accessOnlineReportAnalyzer;oracle.epm.essbasestudio.cpadmin;/;/EssbaseCluster-1;oracle.bi.publisher.developReport;oracle.bi.presentation.catalogmanager.manageCatalog;_all_;oracle.bi.publisher.accessExcelReportAnalyzer;_all_;EPM_Essbase_Calculate;oracle.bi.publisher.developDataModel;EPM_Essbase_Filter;oracle.epm.essbasestudio.viewer;oracle.bi.publisher.runReportOnline;oracle.bi.publisher.scheduleReport;oracle.epm.financialreporting.administerReporting;_all_;EPM_Calc_Manager_Designer;oracle.epm.financialreporting.accessReporting;EPM_Essbase_Administrator;EPM_Calc_Manager_Administrator;oracle.epm.financialreporting.scheduleBatch;oracle.bi.server.impersonateUser;oracle.epm.financialreporting.editReport;oracle.epm.financialreporting.editBook;/EssbaseCluster-1'
permission can not query user population.