About
A simple form (ie not Oracle Apex - Tabular Form)
Articles Related
Creation
Steps
Populating
A form can be populated either:
- on load with PL/SQL
- or with an Automatic Row Fetch
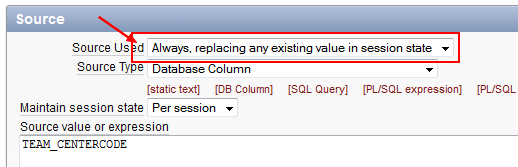
Automatic Row Fetch
- Step 1 - Create an HTML region (to serve as a container for your page items).
- Step 2 - Create items to display in the region (Always overrides the cache value)
- Step 3 - Create an automatic row fetch processes
Programmatically
- Step 1 - Create an HTML region (to serve as a container for your page items).
- Step 2 - Create items to display in the region (Only when current value in session state is null)
- Step 3 - Populate the form programmatically with a PL/SQL process that executes (or fire) on a before Onload - Before Regions.
Example:
FOR C1 in (SELECT ename, sal
FROM emp WHERE ID=:P2_ID)
LOOP
:P2_ENAME := C1.ename;
:P2_SAL := C1.sal;
END LOOP;
where:
- The values of :P2_ENAME and :P2_SAL are being populated
- The value of P2_ID is already known (a hidden session state item named P2_ID)
- C1 is an implicit cursor.
Processing
There are three ways to process a simple form:
- Creating a Process that Contains One or More Insert Statements
- a PL/SQL Package to Process Form Values
Automatic Row Processing (DML)
Process with One or More Statements
One or more processes are created to handle insert, update, and delete actions.
Insertion
To process the insertion of a new row, you create a conditional process of type PL/SQL that executes when the user clicks the Insert button. For example:
BEGIN
INSERT INTO T ( first_name, last_name )
VALUES (:P1_FIRST_NAME, :P1_LAST_NAME);
END;
Update
To process the updating of a row, you create another conditional process of type PL/SQL. For example:
BEGIN
UPDATE T
SET first_name = :P1_FIRST_NAME,
last_name = :P1_LAST_NAME
WHERE ID = :P1_ID;
END;
Delete
To process the deletion of a row, you create a conditional process that executes when the user clicks the Delete button. For example:
BEGIN
DELETE FROM T
WHERE ID = :P1_ID;
END;
PL/SQL Package
If you created a package to handle DML operations, you can call procedures and functions within this package from an After Submit PL/SQL process to process insert, updates, and delete requests.