Cookie - Scope
About
The scope of a cookie name is a calculated property defined by the concatenation of
If the request URL matches the scope (ie domain and path expression), the user agent (browser) will add the cookies in the Cookies header to the request returning it to the server (if the other cookie property (such as expiration date, http only,..) are also valid)
You can have the same name below differents scope.
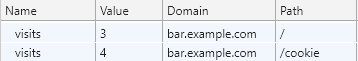
Below you can see that their is 2 cookie named visits below two differents scopes.
Example
For instance:
- A cookie that should be returned to every path and every subdomain of example.com would be set by the server with the following set-cookie response header
Set-Cookie: key=value; Path=/; Domain=example.com
- then when the user-agent (browser) creates an HTTP request for the domain example.com, it will add in the request the following Cookies request headers
Cookies: key=value
Properties
Domain
The domain attribute determines the scope and determine which host (port excluded) are allowed to receive the cookie.
The scope rules are applied top down (ie applied to the domain and all subdomain)
- if the value of the Domain attribute is:
- example.com
- the user agent (browser) will include the cookie to request on the domain and all subdomain. ie
- example.com,
If the domain property of the cookie is:
- the same as the domain of the page you are on, it's a first-party cookie.
- different, it is a third-party cookie.
More … see The domain property of a cookie in depth
Path
The path attribute is a scope attribute and is matched against the request URL path where:
- / means all paths including the root
The default value of the path is the parent of the last name:
- If the URL of the request is https://example.com/foo/bar
- the default scope/cookie path is /foo
If several cookies shares the same name with different path, a list of values is returned ordered by scope order. For instance, suppose that
- there is two cookies with the same name: visits
- their respective path are:
- /
- /cookie
- their respective value are:
- 3
- 2
- a call to https://example.com/cookie
- will result in the following cookie header:
Cookie: visits=2; visits=3
As seen in the Cookie value, there is no way to know the path of the values.