File System - Cluster (File | Sector Cluster)
About
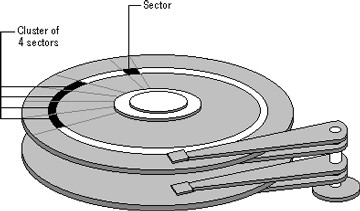
A cluster is a group of hard drive sectors that is addressed as one logical persistent unit by the operating system file system to read and write a file.
In computer file systems, a cluster is the unit of disk space allocation for files and directories.
A cluster represents the smallest amount of disk space that can be used to hold a file.
To reduce the overhead of managing on-disk data structures, the operating system file system does not allocate individual disk sectors, but contiguous groups of sectors, called clusters.
A cluster need not be physically contiguous on the disk; it may span more than one track or, if sector interleaving is used, may even be discontinuous within a track. This should not be confused with fragmentation, as the sectors are still logically contiguous.
Most HDD come from the factory with a low level format where block size = 512 bytes. The filesystem (in this case NTFS) can create cluster sizes of a multiple of 512 (with a default of 4k or 8 blocks).
- A cluster is defined at the operating system file system level (logical)
- A sector is defined at the disk level (physical).
Feature
The cluster allows the OS file system to optimize the administration of disk data independently of the disk sector size set by the hardware disk controller.
Size
Clusters are referenced under Windows as the Allocation Unit Size for the file system.
For instance, NTFS under Windows NT 4.0 and later versions of Windows is 4 kilobytes (KB). More see Windows Cluster Size
Balance between file and cluster size
A cluster is the smallest logical amount of disk space that can be allocated to hold a file. Storing small files on a filesystem with large clusters will therefore waste disk space; such wasted disk space is called slack space. For cluster sizes which are small versus the average file size, the wasted space per file will be statistically about half of the cluster size; for large cluster sizes, the wasted space will become greater. However, a larger cluster size reduces bookkeeping overhead and fragmentation, which may improve reading and writing speed overall.
Typical cluster sizes range from 1 sector (512 B) to 128 sectors (64 KiB).
Fragmentation
Because cluster are logical unit used by the OS file system, they can be anywhere on the disk.
If you want to have them next to each other, you need to perform a defragmentation.