About
The Domain Name System (DNS) 1) is a database of name. It's naming system (service).
It holds naming information for some kind of object (not only but mainly host)
DNS can be seen as the phone book of the internet, it permits to get:
An often-used analogy to explain the Domain Name System is that it serves as the phone book for the Internet by translating human-friendly computer names into IP addresses.
Example
For example:
- the domain name www.example.com
- translates to the addresses:
This is called a DNS lookup (forward).
Anatomy of a query
- A client application will:
- make a connection to a nameserver daemons (service) (generally on port 53)
- send a query
- The nameserver will:
- try to resolve locally the query based with its resolver library
- if not successful, it will send the query to other nameservers, called root nameservers
Architecture
A DNS has the following major components:
- domain name space that defines a tree structure of name
- resources record that defined data associated with the names.
- name servers are server programs which hold information:
- about the domain tree's structure
- resolver. they are programs that extract information from name servers in response to client requests.
where:
- record (A, AAAA,…)
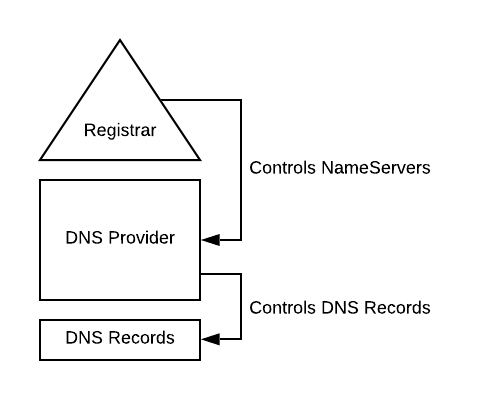
Provider
You buy a apex domain to a provider that will also gives you access to their DNS server in order to manage the DNS record of your domain (called a DNS zone).
You may migrate them to third party. For instance, if you become CloudFlare customer, you need to design their DNS servers as the server of your domain.
With geodns:
- https://dyn.com/ (Pricey ?)
- used by JSdeliver:
- https://ns1.com/ - 26 Dns Pop
- Cloud DNS 35 Dns Pop
- GCore - 108 Dns Pop
Record
Management
Query
A query against a DNS database is called a lookup
The two most known client are:
Local
Locally, the DNS resolver will first check the host file
Check
- The NS record, see server check
Cache
GeoDNS
The DNS responds with a IP dependent of your location. This is used to build a cdn.
Support
With A DNS problem, don't forget to flush your DNS cache.