Definition
An event is a timed observed physical reality described by:
- space (location)
- participant.
The observations describing the event are defined by the nature or physics of the observable, the observation model, and the observer.
An event is the result of an observation.
In business processing, a event is a row in fact table that has a time (dimension) to form time serie
Because events are immutable, they are the cornerstone of every analytics application.
Design system will threat Events as 1st class citizens.
In an event driven architecture:
- the events are facts.
- Events are the notifications (trigger) for transition.
Events are facts that tell a story.
Type
Event may be categorized by the fact that they follow:
- or not
Status / Lifecycle event
A lifecycle event is an event with a status that follows a status (ie state / lifecycle) such as in a business process
Free-form event
In a free-form event, there is no state.
Example:
- events in a graphical user interface (GUI) application, such as keyboard actions, mouse actions, and scroll actions
The schema is fixed for a couple of fields such as:
- event name
- and timestamp
but is mostly unstructured (known as schema-on-read) meaning that:
- The properties/attributes are not fixed and depend heavily on:
- The code that creates them (a property may be added for the purpose of a report)
- The properties may just be not available at the time, the event is created
Handler
An event handler is a function that process events,
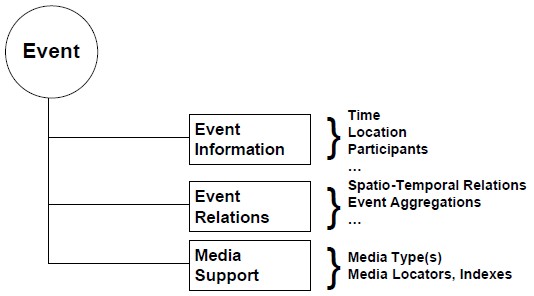
Conceptual Model
- Event model handles complex spatio-temporal reasoning and the semantic unification of heterogeneous multimedia
- Event tagging incorporates humans in the event detection process
Concept
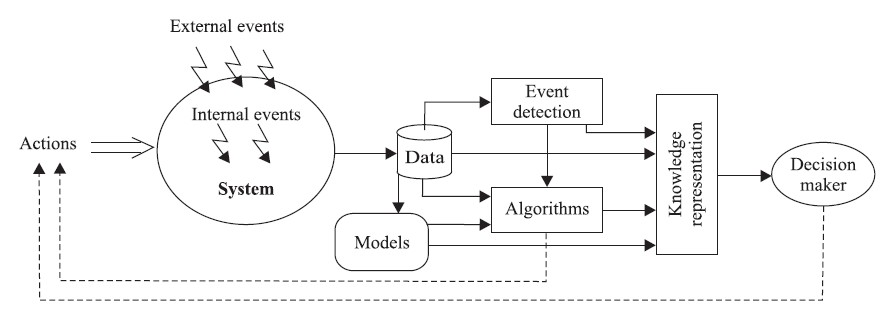
The ability to track event causality and consequences is an essential step toward online decision support and important challenge for new algorithms for event mining. In some cases the results of the algorithms can be directly applied to the system (for example the event based control algorithms).
Many monitoring problems can be also stated as the problem of detecting a change in the parameters of a system called event detection.
Another important concept are event processing networks (EPN) such networks consist of event processing agents called event sources, event processors and event viewers. EPN have been applied for computer network monitoring.
Sometimes, it is impossible to observe the events directly. In such cases the data are stored in databases in form of time series. This data represents observations of the system in selected points. The observations are analyzed by the system and alarms are generated in case of abrupt changes in the values of observations.