About
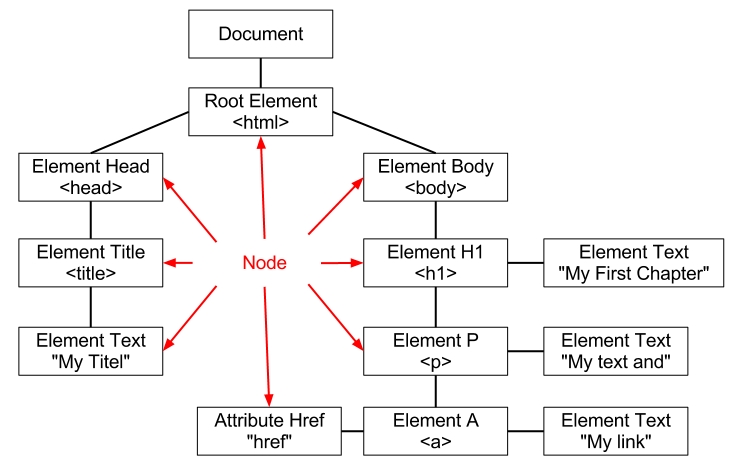
The DOM presents an (XML|HTML) document as a tree-structure.
A DOM has a standard tree structure, where each node contains one of the components from an XML structure.
Generally, the vast majority of nodes in a DOM tree will be Element and Text nodes.
The two most common types of nodes are:
- and text nodes.
The nodes in the node tree have a hierarchical relationship to each other.
See also the root node
Articles Related
Example
<html>
<head>
<title>My Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First chapter</h1>
<p>My Text and<a href="gerardnico.html">My Link</a></p>
</body>
</html>
DOC: nodeName="#document"
ELEM: nodeName="html" local="html"
ELEM: nodeName="head" local="head"
ELEM: nodeName="title" local="title"
TEXT: nodeName="#text" nodeValue="My Title"
ELEM: nodeName="body" local="body"
ELEM: nodeName="h1" local="h1"
TEXT: nodeName="#text" nodeValue="My First chapter"
ELEM: nodeName="p" local="p"
TEXT: nodeName="#text" nodeValue="My Text and"
ELEM: nodeName="a" local="a"
ATTR: nodeName="href" local="href" nodeValue="gerardnico.html"
TEXT: nodeName="#text" nodeValue="gerardnico.html"
TEXT: nodeName="#text" nodeValue="My Link"
Traversal operation
see DOM - Traversal