About
The Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is a framework that determines if the sender of a email transaction is valid for a domain name.
Usage / Goal
It's part of the email authentication framework with DKIM where the goal is to:
- prevent email spoofing
- and reduce unsollicited emails (spam).
How it works?
When a client tries to transmit a mail message to a server, it identifies itself with:
- an IP address due to the TCP connection
- a hostname with the EHLO command
- and an email called the sender with the MAIL command.
To determine if the sender is authorized to send an email, the smtp server:
- will lookup a TXT record known as the SPF record that starts with v=spf1
- read it and determine if the host is authorized to send email for the domain of the sender.
Example of Spf records
v=spf1 is a prefix that you will find in all records that permits to select the record.
- -all: The domain sends no mail at all.
"v=spf1 -all"
- Allow the host in the domain's MXes record to send mail for the domain, prohibit all others.
"v=spf1 mx -all"
- +all Allow all hosts - The domain owner thinks that SPF is useless and/or doesn't care.
"v=spf1 +all"
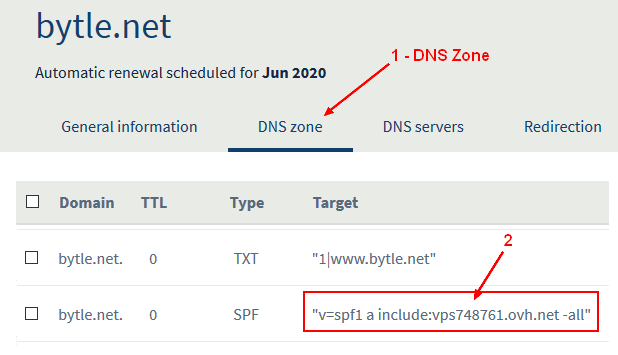
Example of SPF dns record in the DNS zone provided by a domain registrar.
What is a SPF record?
The SPF dns record describes the set of hosts that are designated as outbound mailers for the domain. It determines which server(s) may send an email for a domain.
The SPF record value defines:
- the mechanism of validation (where a validator should get the IP of the server back)
- and a qualifier attached (what actions to take if the validation fails)
If you are forwarding email, the sender (ie gmail for instance) does not allow your server to send email on its behalf, you need to use the Sender Rewriting Scheme (SRS)
Syntax
An SPF record 1) is composed of:
- a preffix - v=spf1
- and one or more mechanism_of_validation with its optional qualifier
v=spf1 [[qualifier]mechanism...]
Validation Process
SPF looks up the DNS record for an e-mail's from address's host header.
Evaluation of an SPF record can return any of these results
| Result | Explanation | Intended action |
|---|---|---|
| Pass | The SPF record designates the host to be allowed to send | accept |
| Fail | The SPF record has designated the host as NOT being allowed to send | reject |
| SoftFail | The SPF record has designated the host as NOT being allowed to send but is in transition | accept but mark |
| Neutral | The SPF record specifies explicitly that nothing can be said about validity | accept |
| None | no SPF record at all or no value | accept |
| PermError | syntax or evaluation error (eg. badly formatted SPF record) | unspecified |
| TempError | dns processing error (dns server not reachable) | accept or reject |
Mechanism of validation
Mechanisms can be used to describe the set of hosts which are designated outbound mailers for the domain.
All
- all represents all mechanisms (generally at the end of the SPF record)
# no mail is send by the domain
v=spf1 -all
# Only the mx mechanism
v=spf1 mx -all
# All mechanism are allowed (ie the admin don't care, generally not found)
v=spf1 +all
IP
#Allow any IP address between 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.255.255.
ip4:192.168.0.1/16
# If no prefix-length is given, /32 is assumed
# example
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.1/16 ~all
# any IPv6 address between 1080::8:800:0000:0000 and 1080::8:800:FFFF:FFFF.
ip6:1080::8:800:200C:417A/96
# example
v=spf1 ip6:2001:4860:4000::/36 ~all
A
A: the whole domain
a: the A records for domain are tested (AAAA for ipv6). If the client IP is found among them, this mechanism matches
# the current dns domain is used (all servers defined in A records may send email)
a
A: List of mailers
# list all the outbound mailers in a special A record under mailers.example.com
a:mailers.example.com
Create in the DNS zone multiple A record with the same name but differents IP
mailers.example.com. IN A 191.98.45.225
mailers.example.com. IN A 163.132.95.201
mailers.example.com. IN A 202.0.013.62
Mx
- mx MX record that defines the Exchange email server
# the mx record plus another emails server
mx mx:deferrals.domain.com
Include
include includes:
- a spf record from an other domain (generally stored under the zone spf.domain.com)
- or another other host
Example: include the host example.com
include:example.com
# if example.com has no SPF record, the result is PermError.
Example:
- ovh hosting with the domain mx.ovh.com:
- mailchimp
- and google
v=spf1 include:mx.ovh.com include:servers.mcsv.net include:_spf.google.com ~all
Other
You have also:
- exists
Mechanism Qualifier
Mechanisms can be prefixed with one of four qualifiers
- + - Pass (default)
- - - Fail
- ~ - SoftFail
- ? - Neutral
Example:
"v=spf1 -all"
"v=spf1 a -all"
"v=spf1 a mx -all"
"v=spf1 +a +mx -all"
Google itself uses a softfail
nslookup -q=TXT _netblocks.google.com 8.8.8.8
v=spf1 ... ip4:216.239.32.0/19 ~all
Modifiers
Domains may also define modifiers. Each modifier can appear only once.
redirect | exp
Alignment
SPF alignment is a check that compares:
- the domain of the envelope sender
- the domain of the author (the header From: address)
Alignment examples with their SPF check results.
| Sender | Author (From:) | Strict alignment | Relaxed alignment |
|---|---|---|---|
| [email protected] | [email protected] | Pass | Pass |
| [email protected] | [email protected] | Fail | Pass |
| [email protected] | [email protected] | Fail | Fail |
The type of alignment check can be defined in your DMARC record via the aspf attribute with:
- a s for strict
- a r for relaxed
Test
Online Checker
Library / Command line
Check Dmarc
A parser for SPF and DMARC DNS records https://github.com/domainaware/checkdmarc
SpfQuery / LibSpf
- Install LibSpf and query
# fedora
yum install libspf2
yum install libspf2-progs
# or ubuntu
sudo apt install spfquery
- Query: Don't pass
spfquery -ip=11.22.33.44 [email protected] -helo=spammer.tld
- Query: Pass
spfquery -ip=192.99.55.226 [email protected] -helo=beau.bytle.net
Jspf
jSpf is a Java library In 2023/10/16, v1.0.3, there is a bug, you need the version 1.0.4 minimal
Example: if you download the assembly, you can execute with the following command
java -cp ".\*;.\lib\*" org.apache.james.jspf.impl.SPFQuery --ip 192.99.55.226 --sender [email protected] --helo beau.bytle.net
More … OpenSpf
See OpenSpf
Query
With DNS - nslookup command line, you can query TXT record. You still need to search for the SPF record in the list.
nslookup -type=TXT bytle.net
Server: amplifi.lan
Address: 192.168.135.1
Non-authoritative answer:
bytle.net text =
"v=spf1 a include:vps748761.ovh.net -all"