How is the DOM Document build from an HTML document ?
About
This page is about the construction of the DOM document from a HTML document (ie the XML language is xhtml)
In a HTML context, the DOM is also known as the API for HTML.
Creation
The HTML dom document is created:
- by an xml library
- or by the browser at page load time. (See browser document)
Structure
In a html dom document:
- The html node contains two dom mandatory node:
- head
- and body
- all DOM node are created from the sub html element, as well as a Text node between them.
Example
Base
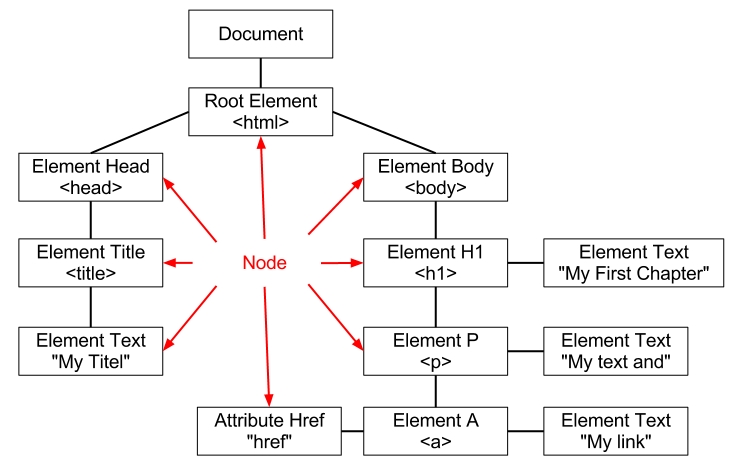
- The following html document
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My titel</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First chapter</h1>
<p>My text and <a href="#link">my link</a></p>
<!-- comment -->
</body>
</html>
- create the following DOM document where:
- The head element creates a head node that contains a title node, which itself contains a Text node with the text “My titel”.
- Similarly, the body element creates a body node that contains an h1 node, a p node, and a comment node.
where the tags are:
- paragraph: <p>
- heading tags: <h1> <h2> <h3> <h4> <h5> <h6>. There are six heading sizes from h1 to h6
- image: <img> self-closes
Second Example
Second example of HTML DOM tree
with the following HTML document
<!-- tells the browser what language it's reading -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<!-- Starts the HTML document -->
<html>
<head>
<title>Sample page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Sample page</h1>
<p>This is a <a href="demo.html">simple</a> sample.</p>
<!-- this is a comment -->
</body>
<!-- Ends the HTML document -->
</html>
we would get the following html document. (not that \n is end of line)
DOCTYPE: html
html
head
#text: '\r '
title
#text: Sample page
#text: '\n '
#text: '\n '
body
#text: '\n '
h1
#text: Sample page
#text: '\n '
p
#text: 'This is a '
a href="demo.html"
#text: simple
#text: sample.
#text: '\n '
#comment: this is a comment
#text: '\n '
Specification
The API for HTML developed by browser vendors were specified and published under the name:
- DOM Level 1 (in 1998)
- DOM Level 2 Core
- and DOM Level 2 HTML.
To avoid exposing Web authors to the complexities of multithreading, the HTML and DOM APIs are designed such that the execution of all scripts is serialized.
An XML DTDs cannot express all the conformance requirements of this specification.
Shadow vs Light DOM
- The light DOM is the HTML written by the user
- While the shadow DOM is a DOM written by the browser
The shadow DOM is used to allow higher functionality such as custom element