SAP BOBJ - Objects and class
About
Each SAP BOBJ - Universe is composed of object contained in a class and you create them using the Universe pane
Object
Web Intelligence users drag objects from the Universe pane across into the Query pane to run queries and create reports with the returned data.
Each object maps to a column or function in a target database, and when used in the Query pane, infers a Select statement. When multiple objects are combined, a Select statement is run on the database including the SQL inferred by each object and applying a default Where clause.
The name of an object should be drawn from the business vocabulary of the targeted user group.
For example, objects used in a universe used by :
- a product manager could be :
- Product,
- Life Cycle,
- or Release Date.
- a financial analyst could contain objects such as :
- Profit Margin
- or Return on Investment.
You use Universe Designer to create the objects that Web Intelligence users include in the Query pane to run their queries.
Classes
Each object is contained in an class
A class is a logical grouping of objects within a universe.
It represents a category of objectsof is the equivalent of a folder in the Windows environment.
The name of a class should indicate the category of the objects that it contains. A class can be divided hierarchically into subclasses.
Articles Related
Object Properties
Business Objects data qualification
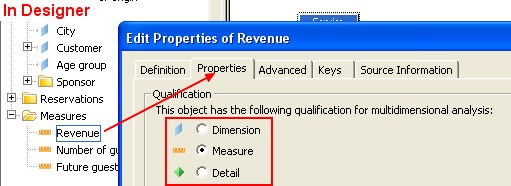
Business Objects qualifies data (objects) used in BusinessObjects in three ways :
- dimension,
- detail,
- or measure.
This qualification shows how data can be used in reports.
Dimension
Dimension objects provide the basis for analysis in a report. Dimension objects typically retrieve character-type data (customer names, city names, etc.), or dates (years, quarters, invoice dates, etc.)
Detail
![]() A detail object is always associated to one dimension object, on which it provides
additional information. For example, Address is a detail object associated to Store.
A detail object is always associated to one dimension object, on which it provides
additional information. For example, Address is a detail object associated to Store.
Measure
![]() Measure objects retrieve numeric data that is the result of calculations on data on the
database. Measure objects are semantically dynamic: the values they return depend
on the objects they are used with. For example, if you include City and Sales
Revenue in a table, revenue per city is calculated. If you include Year and Sales
Revenue, revenue per year is calculated.
Measure objects retrieve numeric data that is the result of calculations on data on the
database. Measure objects are semantically dynamic: the values they return depend
on the objects they are used with. For example, if you include City and Sales
Revenue in a table, revenue per city is calculated. If you include Year and Sales
Revenue, revenue per year is calculated.
Creation Class and Object
Class
- Insert > Class
- Automatically by dragging a table from the table schema into the Universe pane.
Object
- Right click a class in the Universe pane and select Insert Object from the contextual menu.
- Click a table column in the Structure pane. Drag the column across to the Universe pane and drop it at the
desired position in the class hierarchy
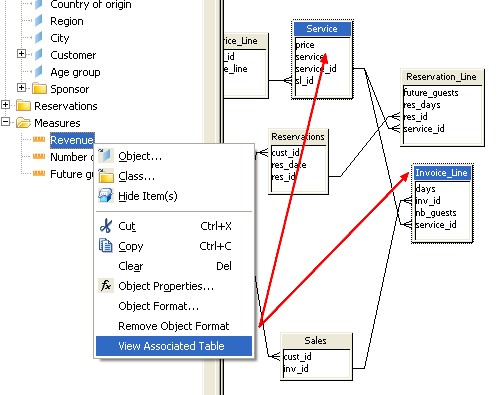
Associated Table
You can view the table in the Structure pane that is used in an object definition from the Universe pane. This can be useful to quickly identify a table used by an object when object names do not easily indicate a specific table.