About
Contexts are a collection of joins which provide a valid query path for SAP BO - Web Intelligence to generate SQL.
Articles Related
Use
You use contexts to resolve join problems that can return too many or too few rows because of the way that tables are linked in the target database.
You need to verify that cardinalitiy are correctly set for all joins in your schema to ensure that you have the correct contexts, and that you have valid join paths.
Setting cardinalitiy can also help you understand how tables are related in the database, and to graphically identify potential join path problems in your schema.
To solve loop
The most common use of contexts is to separate two query paths, so that one query returns data for one fact table, and the other query returns data for another fact table. You use contexts to direct join paths in a schema which contains multiple fact tables. Alias are not appropriate in such schema.
You often use context in schema that contain multiple fact tables (“multiple stars”) that share lookup tables.
To solve chasm and fan traps
Contexts are also used to solve potential BOBJ - Chasm Traps (converging many to one joins). These can occur when two many-to-one join paths converge on a single table. Multiple rows can be returned for a single dimension causing inflated results. Contexts can split out the query so that the correct number of rows are returned for the dimension. Contexts can also be used with BOBJ - Alias to solve BOBJ - Fan Trap (serial many to one joins).
Using contexts to determine AggregateAwareness incompatibility
You can use contexts to exclude objects that are not compatible with an object using the @AggregateAware function in its definition, from being used in a query with the aggregate aware object.
Managing Context
Creation
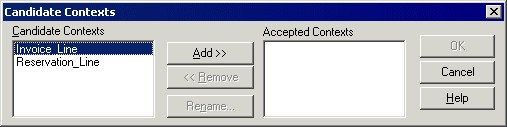
Automatically with Detect Context
Tools > Automated Detection >Detect Contexts
Detect Contexts examines the many to one joins in the schema. It picks up the table that receives converging many to one joins and proposes contexts to separate the queries run on the table.
Manually
- Insert > Context
Edit
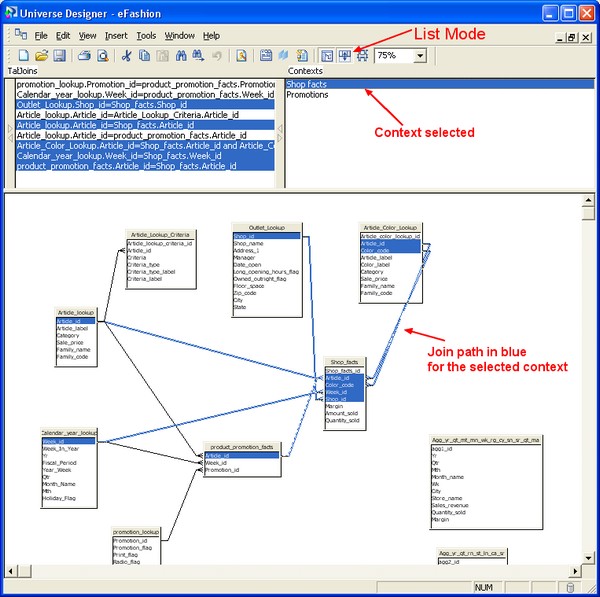
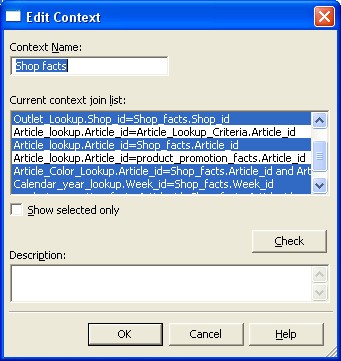
- View > List Mode
- Double click a context name in the Contexts list pane. The Edit Context box appears
Delete
- Ensure that List mode is active (Select View > List Mode).
- Right click a context name in the Contexts list box and select Clear from the contextual menu.
Rename
Click a context and click the Rename button.
Support
One-to-one cardinality preventing context detection
A one-to one-cardinality positioned at the end of a join path can prevent Context Detection in Designer from detecting a context. You resolve this problem by changing the cardinality of the table at the end of the join path to one-to-many.
Incompatible query
Objects from two different contexts are combined in a query. The two Select statements are synchronized to display returned data in separate tables.
To allow incompatible queries to be run in Web Intelligence, you must select the Multiple SQL statements in Designer for each context option.
- File > Parameters.
- Click the SQL tab.
- Select the Multiple SQL statements for each context check box