Oracle Database - Instance (Database Start-up)
About
When you start a database, an instance is created.
An instance is comprised of:
- a memory area called the System Global Area (SGA)
The memory and processes of an instance efficiently manage the associated database's data and serve the database users.
A database has at least one instance. Then you can have many instance of the same database.
An instance also manages other services, such as Oracle XML DB
You can connect to any instance to access information within a cluster database.
Instances are identified by an instance name. The instance name is specified by the INSTANCE_NAME initialization parameter.
Articles Related
How to
Startup
A instance may be mount and open a single database at any point of time. See the Startup command of SQLPlus
SQL> STARTUP
ORACLE instance started.
Total System Global Area 619360256 bytes
Fixed Size 1338280 bytes
Variable Size 377488472 bytes
Database Buffers 234881024 bytes
Redo Buffers 5652480 bytes
Database mounted.
Database opened.
Shutdown
Status
select status from v$instance;
You start up an instance by mounting and opening the database. Doing so makes the database available for any valid user to connect to and perform typical data access operations.
| Status | Mode | Startup Option | Description | Tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOMOUNT | - | NOMOUNT | Does not allow access to the database | usually done only for database creation or the re-creation of control files. |
| Mount | - | MOUNT | Allows DBA activities, but does not allow general access to the database | |
| Open | Restricted mode | RESTRICT | Allow access for database administrators only | |
| Open | Unrestricted | Allow access to all users | ||
| FORCE | Forcing an Instance to Start | |||
| OPEN RECOVER | start an instance, mount a database to the instance, and have the recovery process automatically start |
Restricted
STARTUP RESTRICT
ALTER SYSTEM DISABLE RESTRICTED SESSION;
The parameters of an instance
With SYS_CONTEXT in 10g and higher, you can get almost ALL instances attributes that are available in vinstance but without needed permission.
select
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','HOST'),
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','DB_UNIQUE_NAME')
from dual;
Architecture
One Instance for Each Database
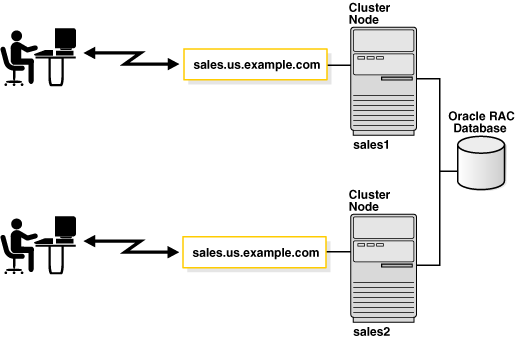
Multiple instances on different computers that share a single physical database
Some hardware architectures allow multiple computers to share access to data, software, or peripheral devices. Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) (Oracle RAC) can take advantage of such architecture by running multiple instances on different computers that share a single physical database.